Difference between revisions of "SinR"
(→Original publications) |
Czschiedrich (talk | contribs) (→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
* '''Mutant:''' TMB079 ''sinR::spec'', GP736 (tetR), available in [[Stülke]] lab | * '''Mutant:''' TMB079 ''sinR::spec'', GP736 (tetR), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
** 1S97 ( ''sinR''::''phleo''), {{PubMed|8422983}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S97&Search=1S97 BGSC] | ** 1S97 ( ''sinR''::''phleo''), {{PubMed|8422983}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S97&Search=1S97 BGSC] | ||
| + | ** GP1672 (''sinR-tasA''::''cat''), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
| + | ** GP1663 (''yghG-sinI-sinR-tasA''), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
| + | |||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 1 November 2013
- Description: transcriptional regulator of post-exponential-phase responses genes
| Gene name | sinR |
| Synonyms | sin, flaD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator of post-exponential-phase responses genes |
| Function | control of biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sinR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SinR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm, Central C-metabolism, Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 12 kDa, 7.177 |
| Gene length, protein length | 333 bp, 111 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sinI, tasA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 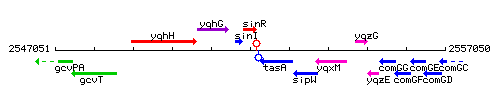
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, transition state regulators, biofilm formation
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, ScoC regulon, Spo0A regulon
The SinR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- transcription regulator of biofilm genes, acts as a true repressor of the tapA-sipW-tasA operon and as an anti-activator (prevents binding of the activator protein RemA) of the epsA-epsB-epsC-epsD-epsE-epsF-epsG-epsH-epsI-epsJ-epsK-epsL-epsM-epsN-epsO operon PubMed
- acts as co-repressor for SlrR PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): SlrR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P06533
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: TMB079 sinR::spec, GP736 (tetR), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Modelling of the SinI/SinR switch
Original publications