SpoIIIAH
Revision as of 14:11, 2 April 2014 by 134.76.38.147 (talk)
- Description: component of the SpoIIIA-SpoIIQ type III secretion system residing in the forespore membrane, required for SigG activation
| Gene name | spoIIIAH |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | part of the transmembrane channel linking the mother cell and the forespore |
| Function | activation of SigG, forespore encasement by the spore coat |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIIAH | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIIIAH | |
| MW, pI | 23 kDa, 4.627 |
| Gene length, protein length | 654 bp, 218 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | accB, spoIIIAG |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 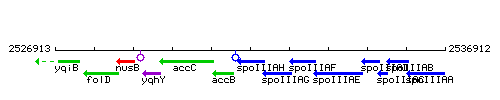
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed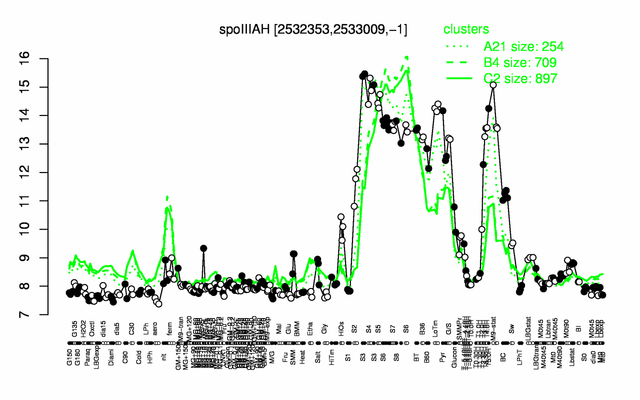
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, sporulation proteins, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24360
Phenotypes of a mutant
- block of sporulation after engulfment
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24360
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- required for forespore encasement by the spore coat PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24360
- UniProt: P49785
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Additional information: the internal promoter is essential for sporulation, it is twice as active as the promoter in front of spoIIIAA, suggesting that SpoIIIAG and SpoIIIAH are required in larger amounts as compared to the other products of the operon PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Charles Moran, Emory University, NC, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Lotte Søgaard-Andersen
Stably bridging a great divide: localization of the SpoIIQ landmark protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 89(6);1019-24
[PubMed:23944268]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications