SpoIIIAD
- Description: component of the SpoIIIA-SpoIIQ type III secretion system residing in the forespore membrane, required for SigG activation
| Gene name | spoIIIAD |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | component of a type III secretion system |
| Function | activation of SigG |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 4.726 |
| Gene length, protein length | 399 bp, 133 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spoIIIAE, spoIIIAC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 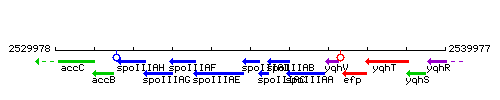
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, sporulation proteins, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24400
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane protein PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P49781
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: expressed during sporulation in the mother cell (SigE) PubMed, switched off by SpoIIID PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Thierry Doan, Cecile Morlot, Jeffrey Meisner, Monica Serrano, Adriano O Henriques, Charles P Moran, David Z Rudner
Novel secretion apparatus maintains spore integrity and developmental gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS Genet: 2009, 5(7);e1000566
[PubMed:19609349]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Amy H Camp, Richard Losick
A novel pathway of intercellular signalling in Bacillus subtilis involves a protein with similarity to a component of type III secretion channels.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 69(2);402-17
[PubMed:18485064]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
N Illing, J Errington
The spoIIIA operon of Bacillus subtilis defines a new temporal class of mother-cell-specific sporulation genes under the control of the sigma E form of RNA polymerase.
Mol Microbiol: 1991, 5(8);1927-40
[PubMed:1766372]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)