Difference between revisions of "EpsG"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[AbrB regulon]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[AbrB regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[EAR riboswitch]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[EAR riboswitch]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[RemA regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SinR regulon]]}} | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SinR regulon]]}} | ||
| Line 116: | Line 117: | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| − | ** [[SinR]]: transcription | + | ** [[SinR]]: transcription anti-activation (prevents binding of [[RemA]]) {{PubMed|23646920}} |
| + | ** [[RemA]]: transcription activation {{PubMed|23646920}} | ||
** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|20817675}} | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|20817675}} | ||
| Line 152: | Line 154: | ||
<pubmed>20374491 20230605 </pubmed> | <pubmed>20374491 20230605 </pubmed> | ||
===Other original publications=== | ===Other original publications=== | ||
| − | <pubmed>15661000,16430695,18047568,11572999 18647168 20817675 21856853 21815947</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>15661000,16430695,18047568,11572999 18647168 20817675 21856853 21815947 23646920</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 24 May 2013
- Description: extracellular polysaccharide synthesis
| Gene name | epsG |
| Synonyms | yveQ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: epsG | |
| Regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 9.379 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1101 bp, 367 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | epsH, epsF |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed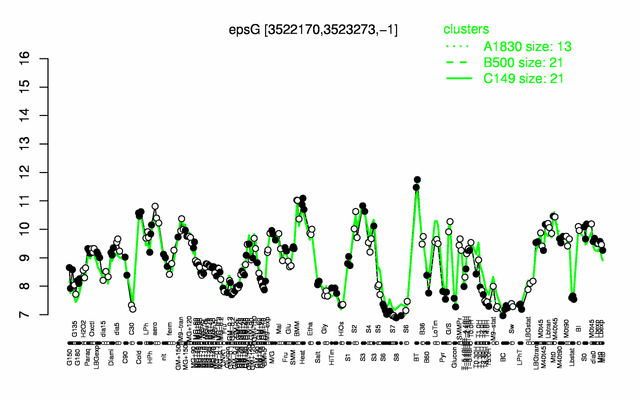
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biofilm formation, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, EAR riboswitch, RemA regulon, SinR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P71056
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- induction by sequestration of SinR by SinI or SlrA PubMed
- the epsA-epsB-epsC-epsD-epsE-epsF-epsG-epsH-epsI-epsJ-epsK-epsL-epsM-epsN-epsO operon is not expressed in a ymdB mutant PubMed
- the amount of the mRNA is substantially decreased upon depletion of RNase Y (this is likely due to the increased stability of the sinR mRNA) PubMed
- the EAR riboswitch (eps-associated RNA switch) located between epsB and epsC mediates processive antitermination and allows expression of the long eps operon PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard Univ., Cambridge, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
The EAR RNA switch
Irnov Irnov, Wade C Winkler
A regulatory RNA required for antitermination of biofilm and capsular polysaccharide operons in Bacillales.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 76(3);559-75
[PubMed:20374491]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Zasha Weinberg, Joy X Wang, Jarrod Bogue, Jingying Yang, Keith Corbino, Ryan H Moy, Ronald R Breaker
Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea, and their metagenomes.
Genome Biol: 2010, 11(3);R31
[PubMed:20230605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Other original publications
Jared T Winkelman, Anna C Bree, Ashley R Bate, Patrick Eichenberger, Richard L Gourse, Daniel B Kearns
RemA is a DNA-binding protein that activates biofilm matrix gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(5);984-97
[PubMed:23646920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Diethmaier, Nico Pietack, Katrin Gunka, Christoph Wrede, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Christina Herzberg, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke
A novel factor controlling bistability in Bacillus subtilis: the YmdB protein affects flagellin expression and biofilm formation.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(21);5997-6007
[PubMed:21856853]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Marc Schaffer, Ulrike Mäder, Christine Diethmaier, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1459-73
[PubMed:21815947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Onuma Chumsakul, Hiroki Takahashi, Taku Oshima, Takahiro Hishimoto, Shigehiko Kanaya, Naotake Ogasawara, Shu Ishikawa
Genome-wide binding profiles of the Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB and its homolog Abh reveals their interactive role in transcriptional regulation.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(2);414-28
[PubMed:20817675]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kazuo Kobayashi
SlrR/SlrA controls the initiation of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 69(6);1399-410
[PubMed:18647168]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Frances Chu, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Bistability and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(2);254-63
[PubMed:18047568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frances Chu, Daniel B Kearns, Steven S Branda, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(4);1216-28
[PubMed:16430695]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Daniel B Kearns, Frances Chu, Steven S Branda, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
A master regulator for biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 55(3);739-49
[PubMed:15661000]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S S Branda, J E González-Pastor, S Ben-Yehuda, R Losick, R Kolter
Fruiting body formation by Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2001, 98(20);11621-6
[PubMed:11572999]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)