Difference between revisions of "EpsG"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || extracellular polysaccharide synthesis | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || extracellular polysaccharide synthesis | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Regulation of this gene in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/biofilm.html Biofilm formation]''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 42 kDa, 9.379 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 42 kDa, 9.379 | ||
Revision as of 10:01, 16 February 2010
- Description: extracellular polysaccharide synthesis
| Gene name | epsG |
| Synonyms | yveQ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | extracellular polysaccharide synthesis |
| Regulation of this gene in SubtiPathways: Biofilm formation | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 9.379 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1101 bp, 367 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | epsH, epsF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 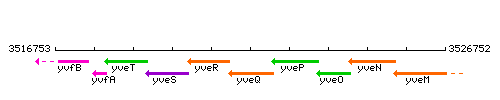
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P71056
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard Univ., Cambridge, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Kazuo Kobayashi
SlrR/SlrA controls the initiation of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 69(6);1399-410
[PubMed:18647168]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Frances Chu, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Bistability and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(2);254-63
[PubMed:18047568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frances Chu, Daniel B Kearns, Steven S Branda, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(4);1216-28
[PubMed:16430695]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Daniel B Kearns, Frances Chu, Steven S Branda, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
A master regulator for biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 55(3);739-49
[PubMed:15661000]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S S Branda, J E González-Pastor, S Ben-Yehuda, R Losick, R Kolter
Fruiting body formation by Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2001, 98(20);11621-6
[PubMed:11572999]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)