BioA
- Description: lysine-8-amino-7-oxononanoate aminotransferase
| Gene name | bioA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | lysine-8-amino-7-oxononanoate aminotransferase |
| Function | biosynthesis of biotin |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: bioA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: bioA | |
| MW, pI | 49 kDa, 5.32 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1344 bp, 448 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | bioF, bioW |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 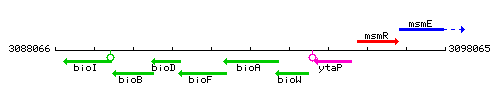
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU30230
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU30230
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: class-III pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU30230
- Structure: 3DRD
- UniProt: P53555
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.6.1.62
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 5350 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2260 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2738 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews: PubMed
Original publications
Scott W Van Arsdell, John B Perkins, R Rogers Yocum, Linda Luan, C Linda Howitt, Nilu Prasad Chatterjee, Janice G Pero
Removing a bottleneck in the Bacillus subtilis biotin pathway: bioA utilizes lysine rather than S-adenosylmethionine as the amino donor in the KAPA-to-DAPA reaction.
Biotechnol Bioeng: 2005, 91(1);75-83
[PubMed:15880481]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J B Perkins, S Bower, C L Howitt, R R Yocum, J Pero
Identification and characterization of transcripts from the biotin biosynthetic operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(21);6361-5
[PubMed:8892842]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Bower, J B Perkins, R R Yocum, C L Howitt, P Rahaim, J Pero
Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis biotin biosynthetic operon.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(14);4122-30
[PubMed:8763940]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)