SpoIIGA
- Description: Pro-SigE protease
| Gene name | spoIIGA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | Pro-SigE protease |
| Function | maturation of SigE |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIGA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIIGA | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 8.552 |
| Gene length, protein length | 927 bp, 309 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | bpr, sigE |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed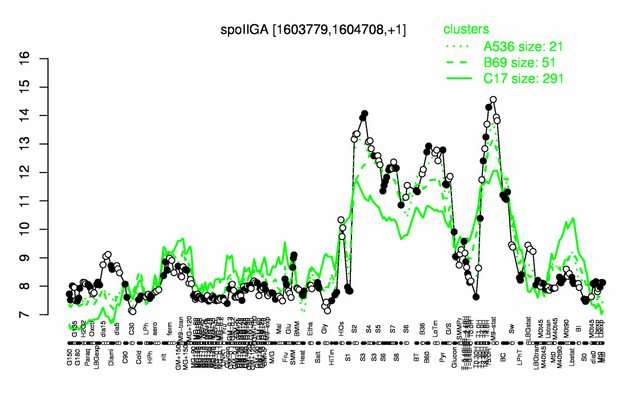
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
proteolysis, sigma factors and their control, sporulation/ other, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: peptidase U4 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P13801
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Steve D Seredick, Barbara M Seredick, David Baker, George B Spiegelman
An A257V mutation in the bacillus subtilis response regulator Spo0A prevents regulated expression of promoters with low-consensus binding sites.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(17);5489-98
[PubMed:19581368]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Amrita Kumar, Charles P Moran
Promoter activation by repositioning of RNA polymerase.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(9);3110-7
[PubMed:18296515]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Masaya Fujita, José Eduardo González-Pastor, Richard Losick
High- and low-threshold genes in the Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(4);1357-68
[PubMed:15687200]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Schyns, C M Buckner, C P Moran
Activation of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIG promoter requires interaction of Spo0A and the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(17);5605-8
[PubMed:9287022]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, P Glaser, J A Hoch
Aspartyl-phosphate phosphatases deactivate the response regulator components of the sporulation signal transduction system in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 19(6);1151-7
[PubMed:8730857]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A E Hofmeister, A Londoño-Vallejo, E Harry, P Stragier, R Losick
Extracellular signal protein triggering the proteolytic activation of a developmental transcription factor in B. subtilis.
Cell: 1995, 83(2);219-26
[PubMed:7585939]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H K Peters, W G Haldenwang
Isolation of a Bacillus subtilis spoIIGA allele that suppresses processing-negative mutations in the Pro-sigma E gene (sigE).
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(24);7763-6
[PubMed:8002606]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Baldus, B D Green, P Youngman, C P Moran
Phosphorylation of Bacillus subtilis transcription factor Spo0A stimulates transcription from the spoIIG promoter by enhancing binding to weak 0A boxes.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(2);296-306
[PubMed:8288522]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T H Bird, J K Grimsley, J A Hoch, G B Spiegelman
Phosphorylation of Spo0A activates its stimulation of in vitro transcription from the Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(4);741-9
[PubMed:8231806]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S W Satola, J M Baldus, C P Moran
Binding of Spo0A stimulates spoIIG promoter activity in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(5);1448-53
[PubMed:1537790]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H K Peters, W G Haldenwang
Synthesis and fractionation properties of SpoIIGA, a protein essential for pro-sigma E processing in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(24);7821-7
[PubMed:1744037]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R M Jonas, E A Weaver, T J Kenney, C P Moran, W G Haldenwang
The Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon encodes both sigma E and a gene necessary for sigma E activation.
J Bacteriol: 1988, 170(2);507-11
[PubMed:2448286]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)