Difference between revisions of "AddB"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease (subunit B) <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease (subunit B), required for efficient survival and replication restart after replication-transcription conflicts <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
<pubmed> 23202527, 20116346 22933559 19542287 25486468 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 23202527, 20116346 22933559 19542287 25486468 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>21809208,8387145,15610857,7746142, 19129187 1646786 10756102 9781875 17570399 20350930 22307084 22383849 21071401 23056615 24682829 24670664 8752329 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>21809208,8387145,15610857,7746142, 19129187 1646786 10756102 9781875 17570399 20350930 22307084 22383849 21071401 23056615 24682829 24670664 8752329 25939832</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:15, 7 May 2015
- Description: ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease (subunit B), required for efficient survival and replication restart after replication-transcription conflicts
| Gene name | addB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease (subunit B)) |
| Function | DNA repair/ recombination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: addB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: AddB | |
| MW, pI | 134 kDa, 5.39 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3498 bp, 1166 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yhjR, addA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 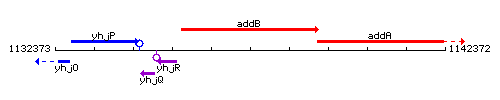
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed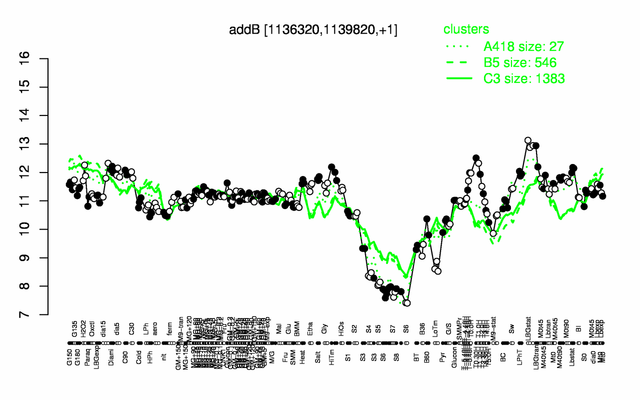
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, genetic competence
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU10620
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU10620
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- the enzyme is functional as a heterodimer of the AddA and AddB subunits, that it is a rapid and processive DNA helicase, and that it catalyses DNA unwinding using one single-stranded DNA motor of 3'→5' polarity located in the AddA subunit PubMed
- the AddB subunit contains a second putative ATP-binding pocket, but this does not contribute to the observed helicase activity and may instead be involved in the recognition of recombination hotspot sequences PubMed
- Protein family: uvrD-like helicase C-terminal domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU10620
- UniProt: P23477
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP1106 (addA-addB, spc), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Mark Dillingham, Bristol, U.K. (homepage)
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Martin Wilkinson, Dale B Wigley
Structural features of Chi recognition in AddAB with implications for RecBCD.
Cell Cycle: 2014, 13(18);2812-20
[PubMed:25486468]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dale B Wigley
Bacterial DNA repair: recent insights into the mechanism of RecBCD, AddAB and AdnAB.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2013, 11(1);9-13
[PubMed:23202527]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph T P Yeeles, Mark S Dillingham
The processing of double-stranded DNA breaks for recombinational repair by helicase-nuclease complexes.
DNA Repair (Amst): 2010, 9(3);276-85
[PubMed:20116346]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gareth A Cromie
Phylogenetic ubiquity and shuffling of the bacterial RecBCD and AddAB recombination complexes.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(16);5076-84
[PubMed:19542287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Samuel Million-Weaver, Ariana Nakta Samadpour, Houra Merrikh
Replication Restart after Replication-Transcription Conflicts Requires RecA in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2015, 197(14);2374-82
[PubMed:25939832]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Neville S Gilhooly, Mark S Dillingham
Recombination hotspots attenuate the coupled ATPase and translocase activities of an AddAB-type helicase-nuclease.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2014, 42(9);5633-43
[PubMed:24682829]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wojciech W Krajewski, Xin Fu, Martin Wilkinson, Nora B Cronin, Mark S Dillingham, Dale B Wigley
Structural basis for translocation by AddAB helicase-nuclease and its arrest at χ sites.
Nature: 2014, 508(7496);416-9
[PubMed:24670664]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jing Zhang, Taciana Kasciukovic, Malcolm F White
The CRISPR associated protein Cas4 Is a 5' to 3' DNA exonuclease with an iron-sulfur cluster.
PLoS One: 2012, 7(10);e47232
[PubMed:23056615]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Pierre Nicolas, Ulrike Mäder, Etienne Dervyn, Tatiana Rochat, Aurélie Leduc, Nathalie Pigeonneau, Elena Bidnenko, Elodie Marchadier, Mark Hoebeke, Stéphane Aymerich, Dörte Becher, Paola Bisicchia, Eric Botella, Olivier Delumeau, Geoff Doherty, Emma L Denham, Mark J Fogg, Vincent Fromion, Anne Goelzer, Annette Hansen, Elisabeth Härtig, Colin R Harwood, Georg Homuth, Hanne Jarmer, Matthieu Jules, Edda Klipp, Ludovic Le Chat, François Lecointe, Peter Lewis, Wolfram Liebermeister, Anika March, Ruben A T Mars, Priyanka Nannapaneni, David Noone, Susanne Pohl, Bernd Rinn, Frank Rügheimer, Praveen K Sappa, Franck Samson, Marc Schaffer, Benno Schwikowski, Leif Steil, Jörg Stülke, Thomas Wiegert, Kevin M Devine, Anthony J Wilkinson, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker, Uwe Völker, Philippe Bessières, Philippe Noirot
Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis.
Science: 2012, 335(6072);1103-6
[PubMed:22383849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kayarat Saikrishnan, Joseph T Yeeles, Neville S Gilhooly, Wojciech W Krajewski, Mark S Dillingham, Dale B Wigley
Insights into Chi recognition from the structure of an AddAB-type helicase-nuclease complex.
EMBO J: 2012, 31(6);1568-78
[PubMed:22307084]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Natalia Fili, Christopher P Toseland, Mark S Dillingham, Martin R Webb, Justin E Molloy
A single-molecule approach to visualize the unwinding activity of DNA helicases.
Methods Mol Biol: 2011, 778;193-214
[PubMed:21809208]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph T P Yeeles, Emma J Gwynn, Martin R Webb, Mark S Dillingham
The AddAB helicase-nuclease catalyses rapid and processive DNA unwinding using a single Superfamily 1A motor domain.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(6);2271-85
[PubMed:21071401]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Natali Fili, Gregory I Mashanov, Christopher P Toseland, Christopher Batters, Mark I Wallace, Joseph T P Yeeles, Mark S Dillingham, Martin R Webb, Justin E Molloy
Visualizing helicases unwinding DNA at the single molecule level.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(13);4448-57
[PubMed:20350930]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph T P Yeeles, Richard Cammack, Mark S Dillingham
An iron-sulfur cluster is essential for the binding of broken DNA by AddAB-type helicase-nucleases.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(12);7746-55
[PubMed:19129187]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Joseph T P Yeeles, Mark S Dillingham
A dual-nuclease mechanism for DNA break processing by AddAB-type helicase-nucleases.
J Mol Biol: 2007, 371(1);66-78
[PubMed:17570399]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Alexander Serganov, Yu-Ren Yuan, Olga Pikovskaya, Anna Polonskaia, Lucy Malinina, Anh Tuân Phan, Claudia Hobartner, Ronald Micura, Ronald R Breaker, Dinshaw J Patel
Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs.
Chem Biol: 2004, 11(12);1729-41
[PubMed:15610857]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F Chédin, S D Ehrlich, S C Kowalczykowski
The Bacillus subtilis AddAB helicase/nuclease is regulated by its cognate Chi sequence in vitro.
J Mol Biol: 2000, 298(1);7-20
[PubMed:10756102]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F Chédin, P Noirot, V Biaudet, S D Ehrlich
A five-nucleotide sequence protects DNA from exonucleolytic degradation by AddAB, the RecBCD analogue of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 29(6);1369-77
[PubMed:9781875]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B J Haijema, R Meima, J Kooistra, G Venema
Effects of lysine-to-glycine mutations in the ATP-binding consensus sequences in the AddA and AddB subunits on the Bacillus subtilis AddAB enzyme activities.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(17);5130-7
[PubMed:8752329]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B J Haijema, L W Hamoen, J Kooistra, G Venema, D van Sinderen
Expression of the ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease of Bacillus subtilis is under competence-mediated control.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 15(2);203-11
[PubMed:7746142]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Kooistra, B J Haijema, G Venema
The Bacillus subtilis addAB genes are fully functional in Escherichia coli.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 7(6);915-23
[PubMed:8387145]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Kooistra, G Venema
Cloning, sequencing, and expression of Bacillus subtilis genes involved in ATP-dependent nuclease synthesis.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(12);3644-55
[PubMed:1646786]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)