Difference between revisions of "MecA"
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU11520&redirect=T BSU11520] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/mecA.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/mecA.html] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 95: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU11520&redirect=T BSU11520] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 2 April 2014
- Description: buffering protein for development, dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression , targets ComK and ComS to ClpC-ClpP degradation machine (in log Phase), inhibits the transcriptional activity of Spo0A∼P by direct interaction
| Gene name | mecA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | adaptor protein |
| Function | control of ComK degradation, regulation of competence |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mecA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MecA | |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 4.209 |
| Gene length, protein length | 654 bp, 218 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yjbE, coiA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 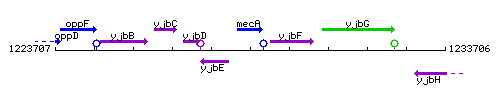
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
genetic competence, proteolysis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11520
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YpbH
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11520
- UniProt: P37958
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP813 (spc), GP814 (aphA3) both available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Noël Molière, Kürşad Turgay
General and regulatory proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Subcell Biochem: 2013, 66;73-103
[PubMed:23479438]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Aurelia Battesti, Susan Gottesman
Roles of adaptor proteins in regulation of bacterial proteolysis.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2013, 16(2);140-7
[PubMed:23375660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Janine Kirstein, Noël Molière, David A Dougan, Kürşad Turgay
Adapting the machine: adaptor proteins for Hsp100/Clp and AAA+ proteases.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(8);589-99
[PubMed:19609260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original Publications
Jing Liu, Ziqing Mei, Ningning Li, Yutao Qi, Yanji Xu, Yigong Shi, Feng Wang, Jianlin Lei, Ning Gao
Structural dynamics of the MecA-ClpC complex: a type II AAA+ protein unfolding machine.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(24);17597-608
[PubMed:23595989]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Prepiak, Melissa Defrancesco, Sophia Spadavecchia, Nicolas Mirouze, Mark Albano, Marjan Persuh, Masaya Fujita, D Dubnau
MecA dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression by two different mechanisms.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(4);1014-30
[PubMed:21435029]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Structure and mechanism of the hexameric MecA-ClpC molecular machine.
Nature: 2011, 471(7338);331-5
[PubMed:21368759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Siheng Xiang, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Crystal structure of the MecA degradation tag.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34376-81
[PubMed:19801546]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ziqing Mei, Feng Wang, Yutao Qi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Han Li, Jiawei Wu, Yigong Shi
Molecular determinants of MecA as a degradation tag for the ClpCP protease.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34366-75
[PubMed:19767395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Douglas J Kojetin, Patrick D McLaughlin, Richele J Thompson, David Dubnau, Peter Prepiak, Mark Rance, John Cavanagh
Structural and motional contributions of the Bacillus subtilis ClpC N-domain to adaptor protein interactions.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 387(3);639-52
[PubMed:19361434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Daria Julkowska, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Krzysztofa Nagorska, Agnieszka Sekowska, I Barry Holland, Simone J Séror
Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 2);398-412
[PubMed:19202088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter Prepiak, David Dubnau
A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP.
Mol Cell: 2007, 26(5);639-47
[PubMed:17560370]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Janine Kirstein, Tilman Schlothauer, David A Dougan, Hauke Lilie, Gilbert Tischendorf, Axel Mogk, Bernd Bukau, Kürşad Turgay
Adaptor protein controlled oligomerization activates the AAA+ protein ClpC.
EMBO J: 2006, 25(7);1481-91
[PubMed:16525504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tilman Schlothauer, Axel Mogk, David A Dougan, Bernd Bukau, Kürşad Turgay
MecA, an adaptor protein necessary for ClpC chaperone activity.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2003, 100(5);2306-11
[PubMed:12598648]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michiko M Nakano, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber
Spx (YjbD), a negative effector of competence in Bacillus subtilis, enhances ClpC-MecA-ComK interaction.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(5);1341-9
[PubMed:12028382]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Randy M Berka, Jeanette Hahn, Mark Albano, Irena Draskovic, Marjan Persuh, Xianju Cui, Alan Sloma, William Widner, David Dubnau
Microarray analysis of the Bacillus subtilis K-state: genome-wide expression changes dependent on ComK.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 43(5);1331-45
[PubMed:11918817]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marjan Persuh, Ines Mandic-Mulec, David Dubnau
A MecA paralog, YpbH, binds ClpC, affecting both competence and sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(8);2310-3
[PubMed:11914365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, F Hajarizadeh, Y Zhu, P Zuber
Loss-of-function mutations in yjbD result in ClpX- and ClpP-independent competence development of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 42(2);383-94
[PubMed:11703662]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Persuh, K Turgay, I Mandic-Mulec, D Dubnau
The N- and C-terminal domains of MecA recognize different partners in the competence molecular switch.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 33(4);886-94
[PubMed:10447896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ogura, L Liu, M Lacelle, M M Nakano, P Zuber
Mutational analysis of ComS: evidence for the interaction of ComS and MecA in the regulation of competence development in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 32(4);799-812
[PubMed:10361283]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, J Hahn, J Burghoorn, D Dubnau
Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor.
EMBO J: 1998, 17(22);6730-8
[PubMed:9890793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, V Dartois, F Kunst, M L Herbaud, F Denizot, G Rapoport
ClpP of Bacillus subtilis is required for competence development, motility, degradative enzyme synthesis, growth at high temperature and sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 27(5);899-914
[PubMed:9535081]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, L W Hamoen, G Venema, D Dubnau
Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1997, 11(1);119-28
[PubMed:9000055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Hahn, J Bylund, M Haines, M Higgins, D Dubnau
Inactivation of mecA prevents recovery from the competent state and interferes with cell division and the partitioning of nucleoids in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 18(4);755-67
[PubMed:8817496]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Hahn, L Kong, D Dubnau
The regulation of competence transcription factor synthesis constitutes a critical control point in the regulation of competence in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(18);5753-61
[PubMed:8083167]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, D Dubnau
Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5793-7
[PubMed:8016067]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, F Kunst, G Rapoport
MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5788-92
[PubMed:8016066]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, K J Siranosian, A D Grossman, D Dubnau
Sequence and properties of mecA, a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(2);365-73
[PubMed:8412687]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Roggiani, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);4056-63
[PubMed:2113920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)