Difference between revisions of "MecA"
Raphael2215 (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | * '''Description:''' buffering protein for development, dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression , targets [[ComK]] to [[ClpC]]-[[ClpP]] degradation machine (in log Phase), inhibits the transcriptional activity of [[Spo0A]]∼P by direct interaction <br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 9 August 2012
- Description: buffering protein for development, dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression , targets ComK to ClpC-ClpP degradation machine (in log Phase), inhibits the transcriptional activity of Spo0A∼P by direct interaction
| Gene name | mecA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | adaptor protein |
| Function | control of ComK degradation, regulation of competence |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mecA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MecA | |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 4.209 |
| Gene length, protein length | 654 bp, 218 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yjbE, coiA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 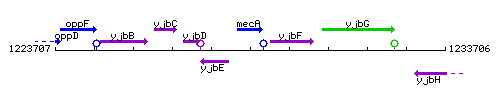
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed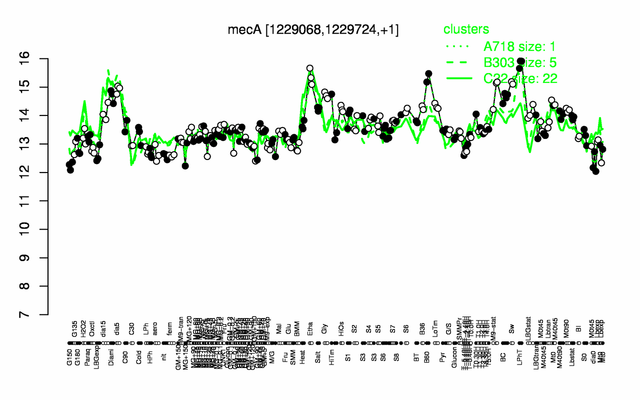
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
genetic competence, proteolysis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YpbH
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P37958
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP813 (spc), GP814 (aphA3) both available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews: PubMed
Original Publications
Additonal publications: PubMed