Difference between revisions of "SpoIIR"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22111992}} | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|20802044,22111992}} |
| − | <pubmed>16497325,7585939,15044948,11849534, 19578359 | + | <pubmed>16497325,7585939,15044948,11849534, 19578359 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:28, 25 November 2011
- Description: required for processing and compartmentalization of pro-SigE
| Gene name | spoIIR |
| Synonyms | ipc-27d, csfX |
| Essential | no |
| Product | morphological chekcpoint for SigE processing |
| Function | control of SigE activation |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 4.737 |
| Gene length, protein length | 672 bp, 224 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywlB, ywlA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 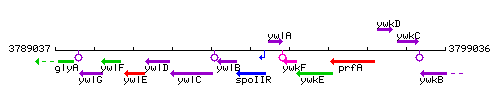
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
sigma factors and their control, sporulation proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36970
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: interacts with and activates the pro-SigE protease SpoIIGA in the intermembrane space between the forespore and the mother cell PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- likely acylated on Thr-27 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39151
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: spoIIR (according to DBTBS)
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed