Difference between revisions of "MecA"
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 53 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 17 April 2014
- Description: buffering protein for development, dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression , targets ComK and ComS to ClpC-ClpP degradation machine (in log Phase), inhibits the transcriptional activity of Spo0A∼P by direct interaction
| Gene name | mecA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | adaptor protein |
| Function | control of ComK degradation, regulation of competence |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mecA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MecA | |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 4.209 |
| Gene length, protein length | 654 bp, 218 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yjbE, coiA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 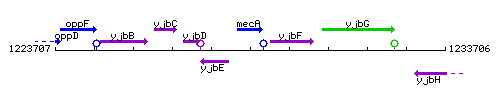
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
genetic competence, proteolysis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11520
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YpbH
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11520
- UniProt: P37958
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 53 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP813 (spc), GP814 (aphA3) both available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Jing Liu, Ziqing Mei, Ningning Li, Yutao Qi, Yanji Xu, Yigong Shi, Feng Wang, Jianlin Lei, Ning Gao
Structural dynamics of the MecA-ClpC complex: a type II AAA+ protein unfolding machine.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(24);17597-608
[PubMed:23595989]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Prepiak, Melissa Defrancesco, Sophia Spadavecchia, Nicolas Mirouze, Mark Albano, Marjan Persuh, Masaya Fujita, D Dubnau
MecA dampens transitions to spore, biofilm exopolysaccharide and competence expression by two different mechanisms.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(4);1014-30
[PubMed:21435029]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Structure and mechanism of the hexameric MecA-ClpC molecular machine.
Nature: 2011, 471(7338);331-5
[PubMed:21368759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Siheng Xiang, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Crystal structure of the MecA degradation tag.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34376-81
[PubMed:19801546]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ziqing Mei, Feng Wang, Yutao Qi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Han Li, Jiawei Wu, Yigong Shi
Molecular determinants of MecA as a degradation tag for the ClpCP protease.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34366-75
[PubMed:19767395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Douglas J Kojetin, Patrick D McLaughlin, Richele J Thompson, David Dubnau, Peter Prepiak, Mark Rance, John Cavanagh
Structural and motional contributions of the Bacillus subtilis ClpC N-domain to adaptor protein interactions.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 387(3);639-52
[PubMed:19361434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Daria Julkowska, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Krzysztofa Nagorska, Agnieszka Sekowska, I Barry Holland, Simone J Séror
Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 2);398-412
[PubMed:19202088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter Prepiak, David Dubnau
A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP.
Mol Cell: 2007, 26(5);639-47
[PubMed:17560370]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Janine Kirstein, Tilman Schlothauer, David A Dougan, Hauke Lilie, Gilbert Tischendorf, Axel Mogk, Bernd Bukau, Kürşad Turgay
Adaptor protein controlled oligomerization activates the AAA+ protein ClpC.
EMBO J: 2006, 25(7);1481-91
[PubMed:16525504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tilman Schlothauer, Axel Mogk, David A Dougan, Bernd Bukau, Kürşad Turgay
MecA, an adaptor protein necessary for ClpC chaperone activity.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2003, 100(5);2306-11
[PubMed:12598648]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michiko M Nakano, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber
Spx (YjbD), a negative effector of competence in Bacillus subtilis, enhances ClpC-MecA-ComK interaction.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(5);1341-9
[PubMed:12028382]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Randy M Berka, Jeanette Hahn, Mark Albano, Irena Draskovic, Marjan Persuh, Xianju Cui, Alan Sloma, William Widner, David Dubnau
Microarray analysis of the Bacillus subtilis K-state: genome-wide expression changes dependent on ComK.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 43(5);1331-45
[PubMed:11918817]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marjan Persuh, Ines Mandic-Mulec, David Dubnau
A MecA paralog, YpbH, binds ClpC, affecting both competence and sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(8);2310-3
[PubMed:11914365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, F Hajarizadeh, Y Zhu, P Zuber
Loss-of-function mutations in yjbD result in ClpX- and ClpP-independent competence development of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 42(2);383-94
[PubMed:11703662]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Persuh, K Turgay, I Mandic-Mulec, D Dubnau
The N- and C-terminal domains of MecA recognize different partners in the competence molecular switch.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 33(4);886-94
[PubMed:10447896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ogura, L Liu, M Lacelle, M M Nakano, P Zuber
Mutational analysis of ComS: evidence for the interaction of ComS and MecA in the regulation of competence development in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 32(4);799-812
[PubMed:10361283]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, J Hahn, J Burghoorn, D Dubnau
Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor.
EMBO J: 1998, 17(22);6730-8
[PubMed:9890793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, V Dartois, F Kunst, M L Herbaud, F Denizot, G Rapoport
ClpP of Bacillus subtilis is required for competence development, motility, degradative enzyme synthesis, growth at high temperature and sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 27(5);899-914
[PubMed:9535081]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, L W Hamoen, G Venema, D Dubnau
Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1997, 11(1);119-28
[PubMed:9000055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Hahn, J Bylund, M Haines, M Higgins, D Dubnau
Inactivation of mecA prevents recovery from the competent state and interferes with cell division and the partitioning of nucleoids in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 18(4);755-67
[PubMed:8817496]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Hahn, L Kong, D Dubnau
The regulation of competence transcription factor synthesis constitutes a critical control point in the regulation of competence in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(18);5753-61
[PubMed:8083167]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, D Dubnau
Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5793-7
[PubMed:8016067]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, F Kunst, G Rapoport
MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5788-92
[PubMed:8016066]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, K J Siranosian, A D Grossman, D Dubnau
Sequence and properties of mecA, a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(2);365-73
[PubMed:8412687]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Roggiani, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);4056-63
[PubMed:2113920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)