SpoIIID
Revision as of 11:28, 14 May 2013 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: transcriptional regulator (repressor or activator) of a subset of sigma-E-dependent genes
| Gene name | spoIIID |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | regulation of mother cell gene expression |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIID | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Asp, Asn, Cell wall | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 9.496 |
| Gene length, protein length | 279 bp, 93 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mbl, usd |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 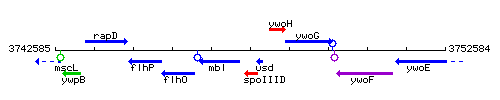
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, sporulation proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SpoIIID regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36420
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binds its DNA targets as a monomeric protein (possible due to the two DNA-binding motifs) PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two DNA-binding regions: HTH at the N-terminus and a basic region near the C-terminus PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 2L0K (complex with DNA)
- UniProt: P15281
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed