YvcJ
- Description: nucleotide-binding protein
| Gene name | yvcJ |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | nucleotide-binding P-loop-containing protein |
| Function | required for the expression of late competence genes |
| MW, pI | 33 kDa, 6.702 |
| Gene length, protein length | 885 bp, 295 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yvcK, yvcI |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 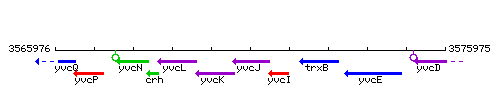
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34770
Phenotypes of a mutant
reduced competence PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binds and hydrolyzes nucleotides, required for the expression of late competence genes (comK, comS) PubMed
- Protein family: UPF0042 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O06973
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: very weak stimuation of expression by citrate and succinate PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector: pGP735 (N-terminal Strep-tag, purification from B. subtilis, for SPINE, in pGP380), available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Görke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Anne Galinier, University of Marseille, France
Your additional remarks
References
Original publications
Publications on the E. coli homolog