KinA
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, phosphorylates Spo0F, part of the phosphorelay
| Gene name | kinA |
| Synonyms | spoIIF, spoIIJ, gsiC, scoB, scoD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | initiation of sporulation |
| Function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay | |
| MW, pI | 68 kDa, 5.491 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1818 bp, 606 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pbpH, patA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 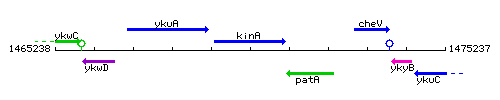
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13990
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of Spo0F
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: interaction with KipI or Sda inhibits autophosphorylation of KinA PubMed
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 2VLG (PAS domain)
- UniProt: P16497
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Prahathees Eswaramoorthy, Masaya Fujita
Systematic domain deletion analysis of the major sporulation kinase in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1744-8
[PubMed:20081035]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Prahathees Eswaramoorthy, Tao Guo, Masaya Fujita
In vivo domain-based functional analysis of the major sporulation sensor kinase, KinA, in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(17);5358-68
[PubMed:19561131]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kazuo Kobayashi, Ritsuko Kuwana, Hiromu Takamatsu
kinA mRNA is missing a stop codon in the undomesticated Bacillus subtilis strain ATCC 6051.
Microbiology (Reading): 2008, 154(Pt 1);54-63
[PubMed:18174125]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Andrew E Whitten, David A Jacques, Boualem Hammouda, Tracey Hanley, Glenn F King, J Mitchell Guss, Jill Trewhella, David B Langley
The structure of the KinA-Sda complex suggests an allosteric mechanism of histidine kinase inhibition.
J Mol Biol: 2007, 368(2);407-20
[PubMed:17350039]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Masaya Fujita, Richard Losick
Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A.
Genes Dev: 2005, 19(18);2236-44
[PubMed:16166384]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Susan L Rowland, William F Burkholder, Katherine A Cunningham, Mark W Maciejewski, Alan D Grossman, Glenn F King
Structure and mechanism of action of Sda, an inhibitor of the histidine kinases that regulate initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2004, 13(5);689-701
[PubMed:15023339]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sophie J Stephenson, Marta Perego
Interaction surface of the Spo0A response regulator with the Spo0E phosphatase.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(6);1455-67
[PubMed:12067336]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Stephenson, J A Hoch
PAS-A domain of phosphorelay sensor kinase A: a catalytic ATP-binding domain involved in the initiation of development in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2001, 98(26);15251-6
[PubMed:11734624]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Wang, C Fabret, K Kanamaru, K Stephenson, V Dartois, M Perego, J A Hoch
Dissection of the functional and structural domains of phosphorelay histidine kinase A of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(9);2795-802
[PubMed:11292798]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Jiang, W Shao, M Perego, J A Hoch
Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 38(3);535-42
[PubMed:11069677]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Fujita, Y Sadaie
Feedback loops involving Spo0A and AbrB in in vitro transcription of the genes involved in the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Biochem: 1998, 124(1);98-104
[PubMed:9644251]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C E Grimshaw, S Huang, C G Hanstein, M A Strauch, D Burbulys, L Wang, J A Hoch, J M Whiteley
Synergistic kinetic interactions between components of the phosphorelay controlling sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry: 1998, 37(5);1365-75
[PubMed:9477965]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Wang, R Grau, M Perego, J A Hoch
A novel histidine kinase inhibitor regulating development in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1997, 11(19);2569-79
[PubMed:9334321]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y L Tzeng, J A Hoch
Molecular recognition in signal transduction: the interaction surfaces of the Spo0F response regulator with its cognate phosphorelay proteins revealed by alanine scanning mutagenesis.
J Mol Biol: 1997, 272(2);200-12
[PubMed:9299348]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Predich, G Nair, I Smith
Bacillus subtilis early sporulation genes kinA, spo0F, and spo0A are transcribed by the RNA polymerase containing sigma H.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(9);2771-8
[PubMed:1569009]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D Burbulys, K A Trach, J A Hoch
Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay.
Cell: 1991, 64(3);545-52
[PubMed:1846779]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, S P Cole, D Burbulys, K Trach, J A Hoch
Characterization of the gene for a protein kinase which phosphorylates the sporulation-regulatory proteins Spo0A and Spo0F of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(11);6187-96
[PubMed:2509430]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)