Noc
- Description: DNA-binding protein, spatial regulator of cell division to protect the nucleoid, and timing device with an important role in the coordination of chromosome segregation and cell division, Noc and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring Z ring placement
| Gene name | noc |
| Synonyms | yyaA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | effector of nucleoid occlusion |
| Function | control of cell division |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: noc | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.812 |
| Gene length, protein length | 849 bp, 283 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yyaB, rsmG |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 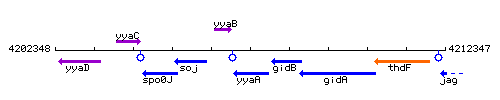
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed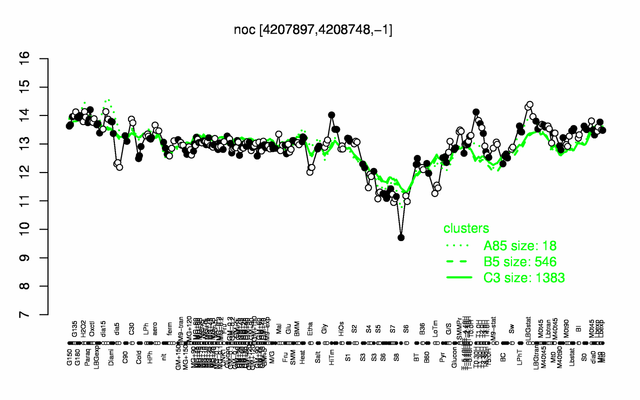
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40990
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binds specific sites on the chromosome PubMed
- Protein family: ParB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): Spo0J
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37524
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: available in the Jeff Errington lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle, UK Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Christopher D A Rodrigues, Elizabeth J Harry
The Min system and nucleoid occlusion are not required for identifying the division site in Bacillus subtilis but ensure its efficient utilization.
PLoS Genet: 2012, 8(3);e1002561
[PubMed:22457634]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ling Juan Wu, Shu Ishikawa, Yoshikazu Kawai, Taku Oshima, Naotake Ogasawara, Jeff Errington
Noc protein binds to specific DNA sequences to coordinate cell division with chromosome segregation.
EMBO J: 2009, 28(13);1940-52
[PubMed:19494834]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Naotake Ogasawara
Bacillus subtilis EzrA and FtsL synergistically regulate FtsZ ring dynamics during cell division.
Microbiology (Reading): 2006, 152(Pt 4);1129-1141
[PubMed:16549676]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ling Juan Wu, Jeff Errington
Coordination of cell division and chromosome segregation by a nucleoid occlusion protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2004, 117(7);915-25
[PubMed:15210112]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mitsuo Ogura, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Yasutaro Fujita, Teruo Tanaka
Whole-genome analysis of genes regulated by the Bacillus subtilis competence transcription factor ComK.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2344-51
[PubMed:11948146]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jörg Sievers, Brian Raether, Marta Perego, Jeff Errington
Characterization of the parB-like yyaA gene of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(4);1102-11
[PubMed:11807071]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)