CggR
- Description: repressor of the glycolytic gapA operon, DeoR family
| Gene name | cggR |
| Synonyms | yvbQ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | central glycolytic genes regulator |
| Function | transcriptional regulator |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cggR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 37,2 kDa,5.68 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1020 bp, 340 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | gapA, araE |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 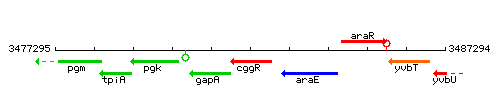
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CggR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33950
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcription repression of the glycolytic gapA operon
- Protein family: sorC transcriptional regulatory family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- DNA binding domain (H-T-H motif) (37–56)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: fructose 1.6-bisphosphate PubMed and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate PubMed act as inducer and result in release of CggR from the DNA
- Interactions:
- active as dimer (according to PubMed)
- Localization: cytoplasma PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 2OKG ( effector binding domain), 3BXH (in complex with fructose-6-phosphate), complex with Fructose-6-Phosphate NCBI, effector binding domain NCBI
- UniProt: O32253
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Database entries: DBTBS
- Additional information:
- The primary mRNAs of the operon are highly unstable. The primary mRNA is subject to processing at the very end of the cggR open reading frame. This results in stable mature gapA and gapA-pgk-tpiA-pgm-eno mRNAs. PubMed The processing event requires the RNase Y PubMed.
- The intracellular concentration of CggR is about 230 nM (according to PubMed).
- The accumulation of the cggR-gapA mRNA is strongly dependent on the presence of the YkzW peptide, due to stabilization of the mRNA PubMed.
- the mRNA is substantially stabilized upon depletion of RNase Y PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP311 (in frame deletion), available in Stülke lab
- SM-NB7 (cggR-spc), available in Anne Galinier's and Boris Görke's labs
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody: available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Nathalie Declerck, Catherine A Royer
Interactions in gene expression networks studied by two-photon fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy.
Methods Enzymol: 2013, 519;203-30
[PubMed:23280112]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew L Ferguson, Dominique Le Coq, Matthieu Jules, Stéphane Aymerich, Ovidiu Radulescu, Nathalie Declerck, Catherine A Royer
Reconciling molecular regulatory mechanisms with noise patterns of bacterial metabolic promoters in induced and repressed states.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(1);155-60
[PubMed:22190493]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol Microbiol. 2011 81(6): 1459-1473. PubMed:21815947