Difference between revisions of "OppA"
(→Biological materials) |
(→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
** BP67 (spc) available in [[Fabian Commichau]]'s lab | ** BP67 (spc) available in [[Fabian Commichau]]'s lab | ||
** 1S118 ( ''oppA''::''spec''), {{PubMed|11267663}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S118&Search=1S118 BGSC] | ** 1S118 ( ''oppA''::''spec''), {{PubMed|11267663}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S118&Search=1S118 BGSC] | ||
| − | ** GP2097 (D(''[[oppA]]-[[oppB]]-[[oppC]]-[[oppD]]-[[ | + | ** GP2097 (D(''[[oppA]]-[[oppB]]-[[oppC]]-[[oppD]]-[[oppF]]'')::''aphA3''), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:42, 20 July 2015
- Description: oligopeptide ABC transporter (binding protein)
| Gene name | oppA |
| Synonyms | spo0KA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | oligopeptide ABC transporter (binding protein) |
| Function | initiation of sporulation, competence development |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: oppA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: OppA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: OppA | |
| MW, pI | 61 kDa, 5.722 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1635 bp, 545 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trpS, oppB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 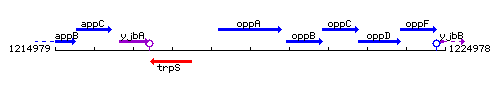
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed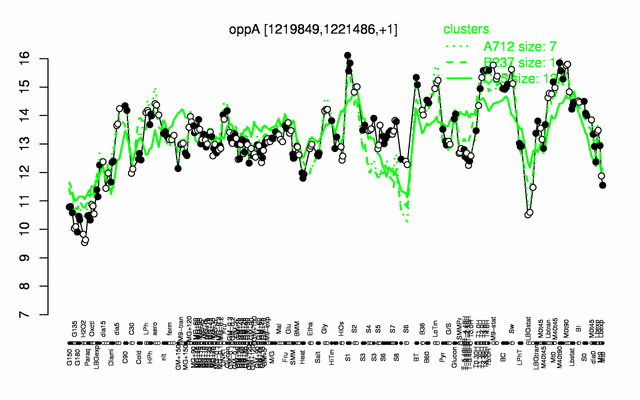
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, utilization of nitrogen sources other than amino acids, genetic competence, phosphorelay, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, ScoC regulon, TnrA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11430
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11430
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: bacterial solute-binding protein 5 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): DppE
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on (Tyr-301 OR Tyr-303) AND Thr-470 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11430
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24141
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- BP67 (spc) available in Fabian Commichau's lab
- 1S118 ( oppA::spec), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GP2097 (D(oppA-oppB-oppC-oppD-oppF)::aphA3), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Boris R Belitsky, Giulia Barbieri, Alessandra M Albertini, Eugenio Ferrari, Mark A Strauch, Abraham L Sonenshein
Interactive regulation by the Bacillus subtilis global regulators CodY and ScoC.
Mol Microbiol: 2015, 97(4);698-716
[PubMed:25966844]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Juri Niño Bach, Marc Bramkamp
Flotillins functionally organize the bacterial membrane.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(6);1205-17
[PubMed:23651456]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Letal I Salzberg, Leagh Powell, Karsten Hokamp, Eric Botella, David Noone, Kevin M Devine
The WalRK (YycFG) and σ(I) RsgI regulators cooperate to control CwlO and LytE expression in exponentially growing and stressed Bacillus subtilis cells.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 87(1);180-95
[PubMed:23199363]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Nicolas Mirouze, Vijay Parashar, Melinda D Baker, David A Dubnau, Matthew B Neiditch
An atypical Phr peptide regulates the developmental switch protein RapH.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6197-206
[PubMed:21908671]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Birgit Voigt, Haike Antelmann, Dirk Albrecht, Armin Ehrenreich, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Stefan Evers, Gerhard Gottschalk, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Thomas Schweder, Michael Hecker
Cell physiology and protein secretion of Bacillus licheniformis compared to Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2009, 16(1-2);53-68
[PubMed:18957862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ken-ichi Yoshida, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Masaki Kinehara, Yo-hei Ohki, Yoshiko Nakaura, Yasutaro Fujita
Identification of additional TnrA-regulated genes of Bacillus subtilis associated with a TnrA box.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(1);157-65
[PubMed:12823818]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Yazgan, G Ozcengiz, M A Marahiel
Tn10 insertional mutations of Bacillus subtilis that block the biosynthesis of bacilysin.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2001, 1518(1-2);87-94
[PubMed:11267663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M S Turner, J D Helmann
Mutations in multidrug efflux homologs, sugar isomerases, and antimicrobial biosynthesis genes differentially elevate activity of the sigma(X) and sigma(W) factors in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(18);5202-10
[PubMed:10960106]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Koide, M Perego, J A Hoch
ScoC regulates peptide transport and sporulation initiation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(13);4114-7
[PubMed:10383984]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J R LeDeaux, J M Solomon, A D Grossman
Analysis of non-polar deletion mutations in the genes of the spo0K (opp) operon of Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1997, 153(1);63-9
[PubMed:9252573]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Koide, J A Hoch
Identification of a second oligopeptide transport system in Bacillus subtilis and determination of its role in sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1994, 13(3);417-26
[PubMed:7997159]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D Z Rudner, J R LeDeaux, K Ireton, A D Grossman
The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(4);1388-98
[PubMed:1899858]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, C F Higgins, S R Pearce, M P Gallagher, J A Hoch
The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1991, 5(1);173-85
[PubMed:1901616]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)