Difference between revisions of "ComFA"
m (→Phenotypes of a mutant) |
|||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| + | knockout has 1000-fold reduction in transformability compared to the wild-type | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 28 May 2015
- Description: membrane-associated ATPase, may provide energy for DNA transport
| Gene name | comFA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-binding protein |
| Function | genetic competence |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: comFA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ComFA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: ComFA | |
| MW, pI | 52 kDa, 9.824 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1389 bp, 463 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | comFB, yviA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 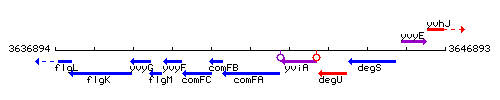
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
genetic competence, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35470
Phenotypes of a mutant
knockout has 1000-fold reduction in transformability compared to the wild-type
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35470
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: helicase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-20, Arg-186, and Arg-446 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35470
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39145
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Miriam Kaufenstein, Martin van der Laan, Peter L Graumann
The three-layered DNA uptake machinery at the cell pole in competent Bacillus subtilis cells is a stable complex.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(7);1633-42
[PubMed:21278288]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Naomi Kramer, Jeanette Hahn, David Dubnau
Multiple interactions among the competence proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 65(2);454-64
[PubMed:17630974]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jeanette Hahn, Berenike Maier, Bert Jan Haijema, Michael Sheetz, David Dubnau
Transformation proteins and DNA uptake localize to the cell poles in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2005, 122(1);59-71
[PubMed:16009133]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hanne Jarmer, Randy Berka, Steen Knudsen, Hans H Saxild
Transcriptome analysis documents induced competence of Bacillus subtilis during nitrogen limiting conditions.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2002, 206(2);197-200
[PubMed:11814663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Londoño-Vallejo, D Dubnau
Mutation of the putative nucleotide binding site of the Bacillus subtilis membrane protein ComFA abolishes the uptake of DNA during transformation.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4642-5
[PubMed:8045895]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Londoño-Vallejo, D Dubnau
Membrane association and role in DNA uptake of the Bacillus subtilis PriA analogue ComF1.
Mol Microbiol: 1994, 13(2);197-205
[PubMed:7984101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Londoño-Vallejo, D Dubnau
comF, a Bacillus subtilis late competence locus, encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent RNA/DNA helicases.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(1);119-31
[PubMed:8412657]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)