Difference between revisions of "LysC"
(→Other original Publications) |
|||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
===Other original Publications=== | ===Other original Publications=== | ||
| − | <pubmed>2168395, 1624109, 2559145, 2557260,12850135 12107147, 17981983 15378759</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>2168395, 1624109, 2559145, 2557260,12850135 12107147, 17981983 15378759 25935345</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 5 May 2015
- Description: aspartokinase II (alpha and beta subunits)
| Gene name | lysC |
| Synonyms | ask, aecA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | aspartokinase II (alpha and beta subunits) |
| Function | biosynthesis of lysine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: lysC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: lysC | |
| MW, pI | 43 kDa, 4.643 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1224 bp, 408 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yslB, uvrC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 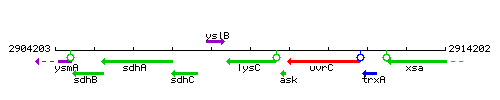
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU28470
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: aspartokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): DapG
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU28470
- Structure: 2RE1 (from Neisseria meningitidis mc58, 40% identity, 58% similarity)
- UniProt: P08495
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.4
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: lysC PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed, also degraded upon ammonium or amino acid starvation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1459 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4406 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1282 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 806 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
The L-box riboswitch
Other original Publications