Difference between revisions of "SpoIIIJ"
(→Original publications) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed>18485064,12813085,18820020,1487728, 23852076,18763711 17114254,11889108 15995216 12586834 19717609 19779460 22864117 24443530 25133632 25313395 25359772 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18485064,12813085,18820020,1487728, 23852076,18763711 17114254,11889108 15995216 12586834 19717609 19779460 22864117 24443530 25133632 25313395 25359772 25855636</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:59, 10 April 2015
- Description: Sec-independent membrane protein translocase, essential for SigG activity at stage III, involved in the assembly of the SpoIIIAH-SpoIIQ complex
| Gene name | spoIIIJ |
| Synonyms | spo0J87 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | membrane protein translocase |
| Function | membrane insertion of proteins and protein secretion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIIJ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIIIJ | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 9.992 |
| Gene length, protein length | 783 bp, 261 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | jag, rnpA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 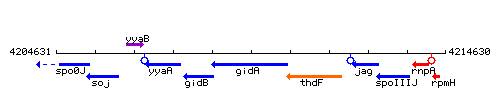
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, sporulation/ other, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU41040
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU41040
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: membrane protein translocase, facilitates insertion of SpoIIIAE into the membrane PubMed
- Protein family: YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 family PubMed
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU41040
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q01625
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1044 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard University, Cambridge, USA homepage
Adriano Henriques, Lisbon, Portugal homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Ross E Dalbey, Peng Wang, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Membrane proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(2);311-30
[PubMed:22688815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Soledad Funes, Frank Kauff, Eli O van der Sluis, Martin Ott, Johannes M Herrmann
Evolution of YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 insertases: three independent gene duplications followed by functional specialization in bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Biol Chem: 2011, 392(1-2);13-9
[PubMed:21194367]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peng Wang, Ross E Dalbey
Inserting membrane proteins: the YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 machinery in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2011, 1808(3);866-75
[PubMed:20800571]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Martin van der Laan, Nico P Nouwen, Arnold J M Driessen
YidC--an evolutionary conserved device for the assembly of energy-transducing membrane protein complexes.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2005, 8(2);182-7
[PubMed:15802250]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications