Difference between revisions of "RecR"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' repair | + | * '''Description:''' required for the formation of [[RecA]] DNA repair centers |
| + | <br/><br/> | ||
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || formation of [[RecA]] DNA repair centers |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || [[DNA repair/ recombination]] | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || [[DNA repair/ recombination]] | ||
| Line 62: | Line 63: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
| Line 71: | Line 69: | ||
* '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | ||
| + | ** required for the formation of [[RecA]] DNA repair centers (together with [[RecO]]) {{PubMed|24891441}} | ||
* '''Protein family:''' recR family (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' recR family (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| Line 144: | Line 143: | ||
<pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed>12884008,17581636, 16479537 24285298 24285298</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12884008,17581636, 16479537 24285298 24285298 24891441</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 11:18, 4 June 2014
- Description: required for the formation of RecA DNA repair centers
| Gene name | recR |
| Synonyms | recM |
| Essential | no |
| Product | formation of RecA DNA repair centers |
| Function | DNA repair/ recombination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: recR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RecR | |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 5.301 |
| Gene length, protein length | 594 bp, 198 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yaaK, yaaL |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 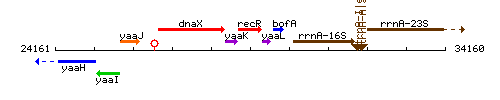
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00210
Phenotypes of a mutant
- drastically reduced survival of mature dormant spores after exposure to ultrahigh vacuum desiccation and ionizing radiation that induce single strand (ss) DNA nicks and double-strand breaks (DSBs) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00210
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: recR family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (homogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00210
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24277
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications