Difference between revisions of "SpoIVA"
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 276 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 10 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 309 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 17 April 2014
- Description: ATPase, spore coat morphogenetic protein, anchors the spore coat to the spore surface via SpoVM
| Gene name | spoIVA |
| Synonyms | spoVP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATPase, basement layer protein for spore coat assembly |
| Function | spore cortex formation and coat assembly |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIVA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIVA | |
| MW, pI | 55 kDa, 4.546 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1476 bp, 492 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | hbs, yphF |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 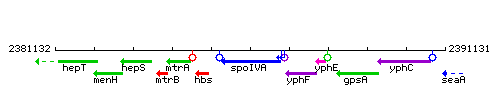
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed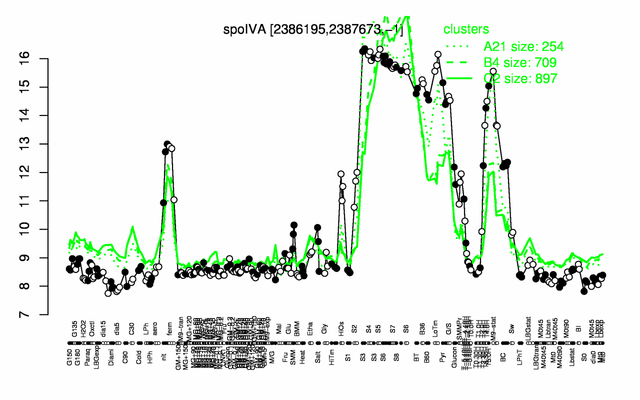
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SpoIVA-dependent proteins of the spore coat basement
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22800
Phenotypes of a mutant
- the spore coat does not localize to the spore surface but self-assembles into aggregates in the mother cell cytoplasm PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU22800
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- uses ATP hydrolysis to drive self-assembly into static filaments PubMed
- ATP hydrolysis drives polymerization of a nucleotide-free filament PubMed
- ploymerization depends on a critical threshold concentration of SpoIVA that is only achieved once the protein is recruited to the surface of the developing spore PubMed
- Protein family:
- belongs to the TRAFAC class of P-loop GTPases, but has lost the ability to bind GTP PubMed
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: contains a Walker A ATPase domain
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- innermost protein of the spore coat basement PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU22800
- Structure:
- UniProt: P35149
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: spoIVA PubMed
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 276 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 10 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 309 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Jean-Philippe Castaing, Attila Nagy, Vivek Anantharaman, L Aravind, Kumaran S Ramamurthi
ATP hydrolysis by a domain related to translation factor GTPases drives polymerization of a static bacterial morphogenetic protein.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2013, 110(2);E151-60
[PubMed:23267091]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Haiyan Qiao, Daniela Krajcikova, Caisheng Liu, Yongjun Li, Hongda Wang, Imrich Barak, Jilin Tang
The interactions of spore-coat morphogenetic proteins studied by single-molecule recognition force spectroscopy.
Chem Asian J: 2012, 7(4);725-31
[PubMed:22262582]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter T McKenney, Patrick Eichenberger
Dynamics of spore coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 83(2);245-60
[PubMed:22171814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Katherine H Wang, Anabela L Isidro, Lia Domingues, Haig A Eskandarian, Peter T McKenney, Kevin Drew, Paul Grabowski, Ming-Hsiu Chua, Samantha N Barry, Michelle Guan, Richard Bonneau, Adriano O Henriques, Patrick Eichenberger
The coat morphogenetic protein SpoVID is necessary for spore encasement in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 74(3);634-49
[PubMed:19775244]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Denisa Müllerová, Daniela Krajčíková, Imrich Barák
Interactions between Bacillus subtilis early spore coat morphogenetic proteins.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2009, 299(1);74-85
[PubMed:19702880]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumaran S Ramamurthi, Richard Losick
ATP-driven self-assembly of a morphogenetic protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2008, 31(3);406-14
[PubMed:18691972]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumaran S Ramamurthi, Katie Rose Clapham, Richard Losick
Peptide anchoring spore coat assembly to the outer forespore membrane in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(6);1547-57
[PubMed:17427285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leif Steil, Mónica Serrano, Adriano O Henriques, Uwe Völker
Genome-wide analysis of temporally regulated and compartment-specific gene expression in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 2);399-420
[PubMed:15699190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patrick Eichenberger, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Erin M Conlon, David Z Rudner, Stephanie T Wang, Caitlin Ferguson, Koki Haga, Tsutomu Sato, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The program of gene transcription for a single differentiating cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS Biol: 2004, 2(10);e328
[PubMed:15383836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Katerina Ragkousi, Patrick Eichenberger, Christiaan van Ooij, Peter Setlow
Identification of a new gene essential for germination of Bacillus subtilis spores with Ca2+-dipicolinate.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(7);2315-29
[PubMed:12644503]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K D Price, R Losick
A four-dimensional view of assembly of a morphogenetic protein during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(3);781-90
[PubMed:9922240]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter J Lewis, Jeffery Errington
Use of green fluorescent protein for detection of cell-specific gene expression and subcellular protein localization during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 4);733-740
[PubMed:8936302]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Pogliano, E Harry, R Losick
Visualization of the subcellular location of sporulation proteins in Bacillus subtilis using immunofluorescence microscopy.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 18(3);459-70
[PubMed:8748030]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C D Webb, A Decatur, A Teleman, R Losick
Use of green fluorescent protein for visualization of cell-specific gene expression and subcellular protein localization during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(20);5906-11
[PubMed:7592342]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Driks, S Roels, B Beall, C P Moran, R Losick
Subcellular localization of proteins involved in the assembly of the spore coat of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1994, 8(2);234-44
[PubMed:8299942]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C M Stevens, R Daniel, N Illing, J Errington
Characterization of a sporulation gene, spoIVA, involved in spore coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(2);586-94
[PubMed:1729247]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Roels, A Driks, R Losick
Characterization of spoIVA, a sporulation gene involved in coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(2);575-85
[PubMed:1729246]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L B Zheng, R Losick
Cascade regulation of spore coat gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1990, 212(4);645-60
[PubMed:1691789]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)