Difference between revisions of "PurF"
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1094 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1094 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4774 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4774 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1287 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1448 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2649 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 17 April 2014
- Description: glutamine phosphoribosyldiphosphate amidotransferase
| Gene name | purF |
| Synonyms | purB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glutamine phosphoribosyldiphosphate amidotransferase |
| Function | purine biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: purF | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: purF | |
| MW, pI | 51 kDa, 5.873 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1428 bp, 476 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | purL, purM |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 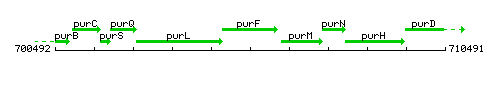
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed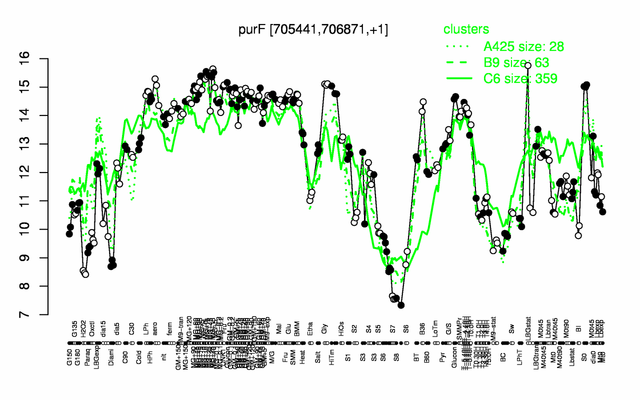
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of nucleotides
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU06490
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU06490
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 5-phospho-beta-D-ribosylamine + diphosphate + L-glutamate = L-glutamine + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate + H2O (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU06490
- UniProt: P00497
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.4.2.14
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1094 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4774 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1287 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1448 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2649 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References