Difference between revisions of "SpoIVFB"
(→Reviews) |
|||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 20836086 23479438 19189971 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 20836086 23479438 19189971 24099006 </pubmed> |
| + | |||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
<pubmed>11959848,9501233,12940997,1577688,12060714,9078383,1942049,10611287,15383836 16818230 19805276 15699190 23585539 23995631 15087499</pubmed> | <pubmed>11959848,9501233,12940997,1577688,12060714,9078383,1942049,10611287,15383836 16818230 19805276 15699190 23585539 23995631 15087499</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 26 November 2013
- Description: intramembrane metalloprotease, processing of pro-sigma-K to active SigK
| Gene name | spoIVFB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | intramembrane metalloprotease |
| Function | processing of pro-sigma-K to active SigK |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIVFB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIVFB | |
| MW, pI | 33 kDa, 8.483 |
| Gene length, protein length | 864 bp, 288 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rplU, spoIVFA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 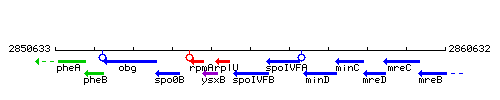
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed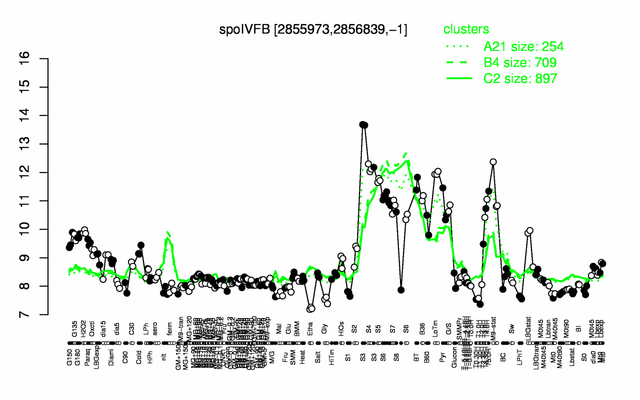
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
sigma factors and their control, proteolysis, sporulation proteins, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27970
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family: peptidase M50B family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- C-terminal cystathionine-beta-synthase (CBS) domain, this domain binds ATP PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: ATP regulates substrate access to the active site and renders cleavage sensitive to the cellular energy level PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P26937
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Yang Zhang, Paul M Luethy, Ruanbao Zhou, Lee Kroos
Residues in conserved loops of intramembrane metalloprotease SpoIVFB interact with residues near the cleavage site in pro-σK.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(21);4936-46
[PubMed:23995631]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ruanbao Zhou, Kangming Chen, Xianling Xiang, Liping Gu, Lee Kroos
Features of Pro-σK important for cleavage by SpoIVFB, an intramembrane metalloprotease.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(12);2793-806
[PubMed:23585539]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ruanbao Zhou, Christina Cusumano, Dexin Sui, R Michael Garavito, Lee Kroos
Intramembrane proteolytic cleavage of a membrane-tethered transcription factor by a metalloprotease depends on ATP.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2009, 106(38);16174-9
[PubMed:19805276]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Nathalie Campo, David Z Rudner
A branched pathway governing the activation of a developmental transcription factor by regulated intramembrane proteolysis.
Mol Cell: 2006, 23(1);25-35
[PubMed:16818230]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leif Steil, Mónica Serrano, Adriano O Henriques, Uwe Völker
Genome-wide analysis of temporally regulated and compartment-specific gene expression in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 2);399-420
[PubMed:15699190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patrick Eichenberger, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Erin M Conlon, David Z Rudner, Stephanie T Wang, Caitlin Ferguson, Koki Haga, Tsutomu Sato, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The program of gene transcription for a single differentiating cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS Biol: 2004, 2(10);e328
[PubMed:15383836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ruanbao Zhou, Lee Kroos
BofA protein inhibits intramembrane proteolysis of pro-sigmaK in an intercompartmental signaling pathway during Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2004, 101(17);6385-90
[PubMed:15087499]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tran C Dong, Simon M Cutting
SpoIVB-mediated cleavage of SpoIVFA could provide the intercellular signal to activate processing of Pro-sigmaK in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(5);1425-34
[PubMed:12940997]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
David Z Rudner, Qi Pan, Richard M Losick
Evidence that subcellular localization of a bacterial membrane protein is achieved by diffusion and capture.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2002, 99(13);8701-6
[PubMed:12060714]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
David Z Rudner, Richard Losick
A sporulation membrane protein tethers the pro-sigmaK processing enzyme to its inhibitor and dictates its subcellular localization.
Genes Dev: 2002, 16(8);1007-18
[PubMed:11959848]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D Z Rudner, P Fawcett, R Losick
A family of membrane-embedded metalloproteases involved in regulated proteolysis of membrane-associated transcription factors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1999, 96(26);14765-70
[PubMed:10611287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
O Resnekov, R Losick
Negative regulation of the proteolytic activation of a developmental transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1998, 95(6);3162-7
[PubMed:9501233]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
O Resnekov, S Alper, R Losick
Subcellular localization of proteins governing the proteolytic activation of a developmental transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Cells: 1996, 1(6);529-42
[PubMed:9078383]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Ricca, S Cutting, R Losick
Characterization of bofA, a gene involved in intercompartmental regulation of pro-sigma K processing during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(10);3177-84
[PubMed:1577688]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Cutting, S Roels, R Losick
Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1991, 221(4);1237-56
[PubMed:1942049]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)