Difference between revisions of "GudB"
(→Original publications) |
(→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP691 (cat), GP1160 (del aphA3) both available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''Mutant:''' GP691 (cat), GP1160 (del aphA3) both available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| − | ** for purification of GudB from ''E. coli'' carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP863 (in [[pGP172]]) available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** for purification of GudB from ''E. coli'' carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP863 (in [[pGP172]]) available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | ** for purification of GudB1 from ''E. coli'' carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP864 (in [[pGP172]]) available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** for purification of GudB1 from ''E. coli'' carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP864 (in [[pGP172]]) available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | ** for ectopic expression of ''gudB'' with its native promoter: pGP900 (in [[pAC5]]), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** for ectopic expression of ''gudB'' with its native promoter: pGP900 (in [[pAC5]]), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | ** wild type ''gudB'', expression in ''B. subtilis'', in [[pBQ200]]: pGP1712, available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** wild type ''gudB'', expression in ''B. subtilis'', in [[pBQ200]]: pGP1712, available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | * '''lacZ fusion:''' pGP651 (in [[pAC5]]), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''lacZ fusion:''' pGP651 (in [[pAC5]]), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | * '''FLAG-tag construct:''' GP1194 (gudB, spc, based on [[pGP1331]]), GP1195 (gudB1, spc, based on [[pGP1331]]), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''FLAG-tag construct:''' GP1194 (gudB, spc, based on [[pGP1331]]), GP1195 (gudB1, spc, based on [[pGP1331]]), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''GFP fusion:''' | * '''GFP fusion:''' | ||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
* '''two-hybrid system:''' | * '''two-hybrid system:''' | ||
| − | * '''Antibody:''' antibody against [[RocG]] recognizes GudB, available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''Antibody:''' antibody against [[RocG]] recognizes GudB, available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 21 July 2013
- Description: trigger enzyme: glutamate dehydrogenase (cryptic in 168 and derivatives)
| Gene name | gudB |
| Synonyms | ypcA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: glutamate dehydrogenase |
| Function | glutamate utilization, control of GltC activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gudB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ammonium/ glutamate | |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 5.582 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1278 bp, 426 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ypdA, ypbH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 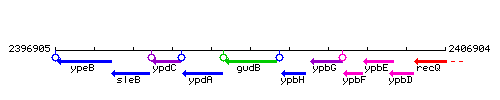
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, transcription factors and their control, trigger enzyme, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22960
Phenotypes of a mutant
- The gene is cryptic. If gudB is activated (gudB1 mutation), the bacteria are able to utilize glutamate as the only carbon source. PubMed
- A rocG gudB mutant is sensitive to ß-lactam antibiotics such as cefuroxime and to fosfomycin due to the downregulation of the SigW regulon PubMed
- transcription profile of a rocG gudB mutant strain: GEO PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamate + H2O + NAD+ = 2-oxoglutarate + NH3 + NADH + H+ (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenases family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): RocG
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-56, Arg-83, and Arg-421 and/or Arg-423 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P50735
- KEGG entry: [4]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.2
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: gudB PubMed
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: GudB is subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP691 (cat), GP1160 (del aphA3) both available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- for purification of GudB from E. coli carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP863 (in pGP172) available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for purification of GudB1 from E. coli carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP864 (in pGP172) available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for ectopic expression of gudB with its native promoter: pGP900 (in pAC5), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- wild type gudB, expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1712, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP651 (in pAC5), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct: GP1194 (gudB, spc, based on pGP1331), GP1195 (gudB1, spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: antibody against RocG recognizes GudB, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Fabian Commichau University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
The GudB protein is active in other legacy B. subtilis strains (e.g. strain 122). Thus, it can be speculated that the ancestral gudB gene was not cryptic, but became so as a product of the "domestication" of B. subtilis 168 in the lab. PubMed
References
Reviews
Original publications
Katrin Gunka, Lorena Stannek, Rachel A Care, Fabian M Commichau
Selection-driven accumulation of suppressor mutants in bacillus subtilis: the apparent high mutation frequency of the cryptic gudB gene and the rapid clonal expansion of gudB(+) suppressors are due to growth under selection.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(6);e66120
[PubMed:23785476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Li-Li Chen, Jia-Le Wang, Yu Hu, Bing-Jun Qian, Xiao-Min Yao, Jing-Fang Wang, Jian-Hua Zhang
Computational design of glutamate dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis natto.
J Mol Model: 2013, 19(4);1919-27
[PubMed:23338837]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Katrin Gunka, Stefan Tholen, Jan Gerwig, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke, Fabian M Commichau
A high-frequency mutation in Bacillus subtilis: requirements for the decryptification of the gudB glutamate dehydrogenase gene.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(5);1036-44
[PubMed:22178973]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yong Heon Lee, Anthony W Kingston, John D Helmann
Glutamate dehydrogenase affects resistance to cell wall antibiotics in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(5);993-1001
[PubMed:22178969]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lope A Flórez, Katrin Gunka, Rafael Polanía, Stefan Tholen, Jörg Stülke
SPABBATS: A pathway-discovery method based on Boolean satisfiability that facilitates the characterization of suppressor mutants.
BMC Syst Biol: 2011, 5;5
[PubMed:21219666]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Katrin Gunka, Joseph A Newman, Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Cecilia Rodrigues, Lorraine Hewitt, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
Functional dissection of a trigger enzyme: mutations of the bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase RocG that affect differentially its catalytic activity and regulatory properties.
J Mol Biol: 2010, 400(4);815-27
[PubMed:20630473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniel R Zeigler, Zoltán Prágai, Sabrina Rodriguez, Bastien Chevreux, Andrea Muffler, Thomas Albert, Renyuan Bai, Markus Wyss, John B Perkins
The origins of 168, W23, and other Bacillus subtilis legacy strains.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(21);6983-95
[PubMed:18723616]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeki Kada, Masahiro Yabusaki, Takayuki Kaga, Hitoshi Ashida, Ken-ichi Yoshida
Identification of two major ammonia-releasing reactions involved in secondary natto fermentation.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2008, 72(7);1869-76
[PubMed:18603778]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Katrin Gunka, Jens J Landmann, Jörg Stülke
Glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: gene expression and enzyme activities evolved to avoid futile cycles and to allow rapid responses to perturbations of the system.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(10);3557-64
[PubMed:18326565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Ingrid Wacker, Jan Schleider, Hans-Matti Blencke, Irene Reif, Philipp Tripal, Jörg Stülke
Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with carbon source-independent glutamate biosynthesis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2007, 12(1-2);106-13
[PubMed:17183217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, A L Sonenshein
Role and regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(23);6298-305
[PubMed:9829940]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)