Difference between revisions of "NadE"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 62: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 116: | Line 110: | ||
* '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]], [[SigB]] {{PubMed|9271869,11544224}} | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]], [[SigB]] {{PubMed|9271869,11544224}} | ||
| − | * '''Regulation:''' induced by stress ([[SigB]]) {{PubMed|11544224}} | + | * '''Regulation:''' |
| + | ** induced by stress ([[SigB]]) {{PubMed|11544224}} | ||
| + | ** induced by antibiotics interacting with the cytoplasmic membrane {{PubMed|22926563}} | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| Line 142: | Line 138: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>9271869,8450306, 19554628,11544224, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>9271869,8450306, 19554628,11544224,22926563 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:25, 29 August 2012
- Description: NH3-dependent NAD+ synthetase
| Gene name | nadE |
| Synonyms | outB, tscBGH, gsp-81 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | NH3-dependent NAD+ synthetase |
| Function | NAD biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: nadE | |
| MW, pI | 30 kDa, 4.888 |
| Gene length, protein length | 816 bp, 272 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ycgI, tmrB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 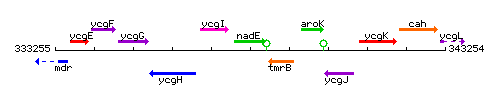
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis of cofactors, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU03130
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + deamido-NAD+ + NH3 = AMP + diphosphate + NAD+ (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: NAD synthetase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 1KQP
- UniProt: P08164
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.3.1.5
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: nadE PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Michaela Wenzel, Bastian Kohl, Daniela Münch, Nadja Raatschen, H Bauke Albada, Leendert Hamoen, Nils Metzler-Nolte, Hans-Georg Sahl, Julia E Bandow
Proteomic response of Bacillus subtilis to lantibiotics reflects differences in interaction with the cytoplasmic membrane.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother: 2012, 56(11);5749-57
[PubMed:22926563]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James A Mobley, Anton Poliakov
Detection of early unfolding events in a dimeric protein by amide proton exchange and native electrospray mass spectrometry.
Protein Sci: 2009, 18(8);1620-7
[PubMed:19554628]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Antelmann, R Schmid, M Hecker
The NAD synthetase NadE (OutB) of Bacillus subtilis is a sigma B-dependent general stress protein.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1997, 153(2);405-9
[PubMed:9271869]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Caramori, S Calogero, A M Albertini, A Galizzi
Functional analysis of the outB gene of Bacillus subtilis.
J Gen Microbiol: 1993, 139(1);31-7
[PubMed:8450306]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)