Difference between revisions of "PnpA"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
| − | <pubmed>11948165,,8825779,19433509, 19327365, 9811656, 14976255,19433509, 15995184, 8825778, 8636041, 15805522, 19193632, 1707536 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>11948165,,8825779,19433509, 19327365, 9811656, 14976255,19433509, 15995184, 8825778, 8636041, 15805522, 19193632, 1707536 19633085 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 07:31, 28 July 2009
- Description: polynucleotide phosphorylase
| Gene name | pnpA |
| Synonyms | comR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) (EC 2.7.7.8) |
| Function | necessary for competence development |
| MW, pI | 77 kDa, 4.89 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2115 bp, 705 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rpsO, ylxY |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 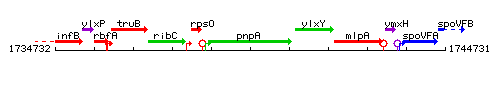
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16690
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 3'-5' exoribonuclease
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 3CDI (protein from E. coli), 3GCM (protein from E. coli, PNPase/RNase E micro-domain/RNA tetragonal crystal form )
- UniProt: P50849
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
required for the expression of late competence genes comG and comK, requirement bypassed by a mecA disruption; may be necessary for modification of the srfA transcript (stabilization or translation activation)
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
David Bechhofer, Mount Sinai School, New York, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Shiyi Yao, David H Bechhofer
Processing and stability of inducibly expressed rpsO mRNA derivatives in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(18);5680-9
[PubMed:19633085]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paula P Cardenas, Begoña Carrasco, Humberto Sanchez, Gintaras Deikus, David H Bechhofer, Juan C Alonso
Bacillus subtilis polynucleotide phosphorylase 3'-to-5' DNase activity is involved in DNA repair.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2009, 37(12);4157-69
[PubMed:19433509]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Salima Nurmohamed, Bhamini Vaidialingam, Anastasia J Callaghan, Ben F Luisi
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli polynucleotide phosphorylase core bound to RNase E, RNA and manganese: implications for catalytic mechanism and RNA degradosome assembly.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 389(1);17-33
[PubMed:19327365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Fabian M Rothe, Christina Herzberg, Eva Wagner, Daniel Hellwig, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Elke Hammer, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2009, 8(6);1350-60
[PubMed:19193632]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Juan Campos-Guillén, Patricia Bralley, George H Jones, David H Bechhofer, Gabriela Olmedo-Alvarez
Addition of poly(A) and heteropolymeric 3' ends in Bacillus subtilis wild-type and polynucleotide phosphorylase-deficient strains.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(14);4698-706
[PubMed:15995184]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Irina A Oussenko, Teppei Abe, Hiromi Ujiie, Akira Muto, David H Bechhofer
Participation of 3'-to-5' exoribonucleases in the turnover of Bacillus subtilis mRNA.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(8);2758-67
[PubMed:15805522]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Gintaras Deikus, Paul Babitzke, David H Bechhofer
Recycling of a regulatory protein by degradation of the RNA to which it binds.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2004, 101(9);2747-51
[PubMed:14976255]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D H Bechhofer, W Wang
Decay of ermC mRNA in a polynucleotide phosphorylase mutant of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(22);5968-77
[PubMed:9811656]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Wang, D H Bechhofer
Properties of a Bacillus subtilis polynucleotide phosphorylase deletion strain.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(8);2375-82
[PubMed:8636041]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Luttinger, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Polynucleotide phosphorylase is necessary for competence development in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 19(2);343-56
[PubMed:8825779]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Mitra, K Hue, D H Bechhofer
In vitro processing activity of Bacillus subtilis polynucleotide phosphorylase.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 19(2);329-42
[PubMed:8825778]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M P Deutscher, N B Reuven
Enzymatic basis for hydrolytic versus phosphorolytic mRNA degradation in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1991, 88(8);3277-80
[PubMed:1707536]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)