Difference between revisions of "PurL"
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| + | ** repressed in the presence of purine nucleotides ([[PurR]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7638212 PubMed] | ||
** repressed in the presence of adenine or adenosine([[PurR]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2536750 PubMed] | ** repressed in the presence of adenine or adenosine([[PurR]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2536750 PubMed] | ||
** repressed in the presence of guanine([[G-box]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3036807 PubMed] | ** repressed in the presence of guanine([[G-box]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3036807 PubMed] | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| + | ** [PurR]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7638212 PubMed] | ||
** [[PurR]]: transcription repression (molecular inducer: PRPP) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2536750 PubMed] | ** [[PurR]]: transcription repression (molecular inducer: PRPP) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2536750 PubMed] | ||
** [[G-box]]: transcription termination/ antitermination ([[riboswitch]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3036807 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12787499 PubMed2] | ** [[G-box]]: transcription termination/ antitermination ([[riboswitch]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3036807 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12787499 PubMed2] | ||
Revision as of 17:08, 11 June 2009
- Description: phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase
| Gene name | purL |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase |
| Function | purine biosynthesis |
| MW, pI | 80 kDa, 4.554 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2226 bp, 742 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | purQ, purF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 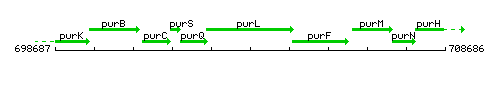
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU06480
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H2O = ADP + phosphate + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FGAMS family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), membrane associated PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P12042
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.3.5.3
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Gerth et al. (2008) Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 190:321-331 PubMed
- Hahne et al. (2008) From complementarity to comprehensiveness - targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches. Proteomics 8: 4123-4136 PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed