Difference between revisions of "RocG"
(→Enzymatic activity of RocG) |
|||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
==Enzymatic activity of RocG== | ==Enzymatic activity of RocG== | ||
| − | <pubmed>18603778,16244435 16195607 ,18326565, 9829940 20630473 21965396 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18603778,16244435 16195607 ,18326565, 9829940 20630473 21965396 25711804</pubmed> |
| + | |||
==Function in the control of [[GltC]] activity== | ==Function in the control of [[GltC]] activity== | ||
<pubmed>15150225,17994626 ,17608797 17183217 20630473 </pubmed> | <pubmed>15150225,17994626 ,17608797 17183217 20630473 </pubmed> | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 3 March 2015
- Description: trigger enzyme: catabolic glutamate dehydrogenase induced by arginine, ornithine or proline, subject to carbon catabolite repression
| Gene name | rocG |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: glutamate dehydrogenase (major) |
| Function | arginine utilization, controls the activity of GltC |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rocG | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RocG | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: rocG | |
| MW, pI | 46.2 kDa, 6.28 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1272 bp, 424 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | rocA, sivA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 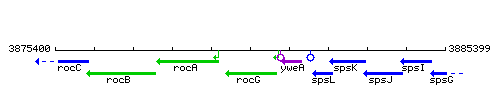
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed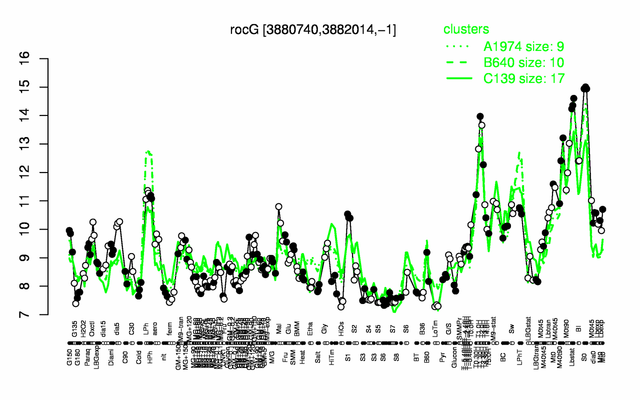
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, transcription factors and their control, trigger enzyme
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, AhrC regulon, CcpA regulon, RocR regulon, SigL regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37790
Phenotypes of a mutant
- Poor growth on complex media such as SP (sporulation medium). No growth in minimal media with arginine as the only carbon source. Rapid accumulation of suppressor mutants (gudB1)
- sensitive to ß-lactam antibiotics such as cefuroxime and to fosfomycin (suppressed by activation of gudB) due to the downregulation of the SigW regulon PubMed
- transcription profile of a rocG gudB mutant strain: GEO PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37790
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamate + H2O + NAD+ = 2-oxoglutarate + NH3 + NADH + H+ (according to Swiss-Prot), controls the activity of the GltC transcription activator PubMed
- Protein family: Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenases family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): GudB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: KM [glutamate] = 2.9 mM, KM [ammonium] = 18 mM PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): NAD+/NADH + H+
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37790
- Structure: 3K92 (super-repressor mutant that is capable of constitutive inactivation of GltC, E93K mutation) PubMed
- UniProt: P39633
- KEGG entry: [4]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.2
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rocG PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Activation by RocR requires binding of RocR to a downstream element PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 16024 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP747 (spc), GP726 (aphA3), GP810 (del tet), GP1157 (cat) all available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- expression of native rocG in B. subtilis: pGP529 (in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab PubMed
- for purification of RocG from E. coli carrying an N-terminal Strep-tag: pGP902 (in pGP172), a series of rocG variants is also available in pGP172, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pWH844: pGP860, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- purification from B. subtilis with an N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, (in pGP380): pGP1709, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Fabian Commichau University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Enzymatic activity of RocG
Function in the control of GltC activity
Expression of rocG
Structural analysis of glutamate dehydrogenase
Bypass of rocG mutations
Additional publications