Difference between revisions of "Eno"
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphoproteins]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphoproteins]]}}, | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki category|[[universally conserved proteins]]}} | + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[universally conserved proteins]]}}, |
| + | [[most abundant proteins]] | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| Line 84: | Line 85: | ||
* '''Kinetic information:''' reversible Michaelis-Menten [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/25885 PubMed] | * '''Kinetic information:''' reversible Michaelis-Menten [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/25885 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''[[Domains]]:''' |
** substrate binding domain (366–369) | ** substrate binding domain (366–369) | ||
* '''Modification:''' phosphorylation on Thr-141 AND Ser-259 AND Tyr-281 AND Ser-325 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17218307 PubMed], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16493705 PubMed], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17726680 PubMed] | * '''Modification:''' phosphorylation on Thr-141 AND Ser-259 AND Tyr-281 AND Ser-325 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17218307 PubMed], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16493705 PubMed], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17726680 PubMed] | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''[[Cofactors]]:''' Mg2+ |
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| Line 142: | Line 143: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| + | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 185: | Line 187: | ||
==Other original publications== | ==Other original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 23420519 17726680, 17218307, 12850135, 19193632, 11489127, 8021172, 17505547, 25885, 20572937 15476816 9988532 ,21803996 22198292 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 23420519 17726680, 17218307, 12850135, 19193632, 11489127, 8021172, 17505547, 25885, 20572937 15476816 9988532 , 21803996 22198292 15378759</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 5 March 2014
- Description: enolase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme, universally conserved protein
| Gene name | eno |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | Yes (PubMed) |
| Product | enolase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: eno | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Eno | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 46,4 kDa, 4.49 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1290 bp, 430 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | yvbK, pgm |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 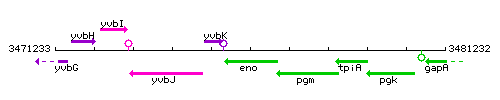
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed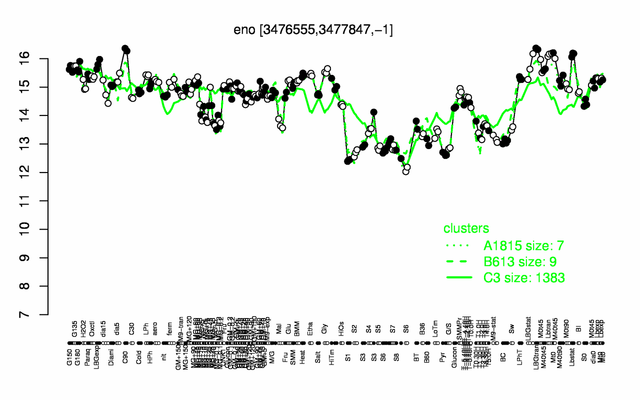
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, essential genes, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins, universally conserved proteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33900
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no growth on LB, requires glucose and malate
- essential according to Kobayashi et al. on LB PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O (according to Swiss-Prot) 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Protein family: enolase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: reversible Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Domains:
- substrate binding domain (366–369)
- Cofactors: Mg2+
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by EDTA PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P37869
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.2.1.11
Additional information
- Enolase is a moonlighting protein. PubMed
- There are indications that this enzyme is an octamer PubMed
- universally conserved protein
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of Eno can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP594 (eno::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- GP599 (eno::erm), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- GP698 (eno-pgm::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- Expression vector:
- pGP1426 (expression of eno in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP1500 (expression of pgm and eno in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP563 (N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP1276 (N-terminal Strep-tag, purification from E. coli, in pGP172), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP93 (N-terminal Strep-tag, purification from B. subtilis, for SPINE, in pGP380), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1215 (chromosomal eno-Strep fusion, spc), purification from B. subtilis, for SPINE, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- see pgk
- GFP fusion:
- pHT315-yfp-eno, available in Mijakovic lab
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct:
- GP1214 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
G H Reed, R R Poyner, T M Larsen, J E Wedekind, I Rayment
Structural and mechanistic studies of enolase.
Curr Opin Struct Biol: 1996, 6(6);736-43
[PubMed:8994873]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Subcellular localization of enolase
Other original publications