Difference between revisions of "DnaA"
(→Labs working on this gene/protein) |
|||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
* [[Peter Graumann]], Freiburg University, Germany [http://www.biologie.uni-freiburg.de/data/bio2/graumann/index.htm homepage] | * [[Peter Graumann]], Freiburg University, Germany [http://www.biologie.uni-freiburg.de/data/bio2/graumann/index.htm homepage] | ||
* [[Alan Grossman]], MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA | * [[Alan Grossman]], MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA | ||
| + | * [[Heath Murray]], Centre for Bacterial Cell Biology, Newcastle, UK[http://www.ncl.ac.uk/camb/staff/profile/heath.murray] | ||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 15 August 2013
- Description: AAA+ ATPase, replication initiation protein
| Gene name | dnaA |
| Synonyms | dnaH, dnaJ, dnaK |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | replication initiation protein |
| Function | DNA replication |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: dnaA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DnaA | |
| MW, pI | 50 kDa, 6.035 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1338 bp, 446 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rpmH, dnaN |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 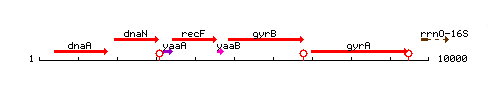
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed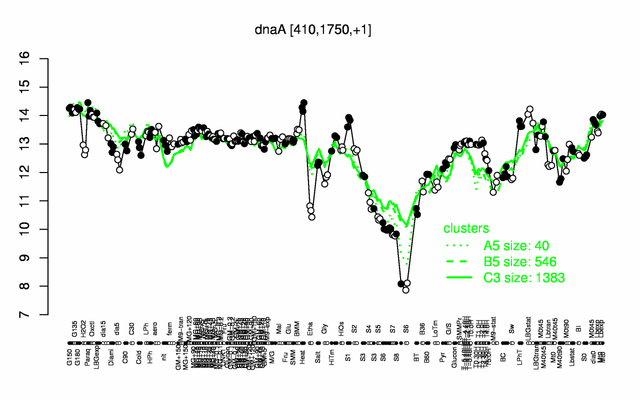
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA replication, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The DnaA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00010
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- binds multiple regions in the oriC region, required for recruitment of proteins needed to load the replicative helicase DnaC
- Protein family: dnaA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: AAA+ domain
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- SirA displaces DnaA from the replication origin PubMed
- YabA inhibits co-operative binding of DnaA to the oriC DNA PubMed
- DnaA helix formation (and thus replication initiation) is inhibited by the interaction of either Soj, YabA or DnaN with the AAA+ domain of DnaA PubMed
- interaction with DnaD inhibits the ability of DnaA to cooperatively bind to DNA PubMed
- Localization:
- throughout the cytoplasm PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05648
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Philippe Noirot, Jouy-en-Josas, France homepage
- Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
- Alan Grossman, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Heath Murray, Centre for Bacterial Cell Biology, Newcastle, UK[4]
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
The DnaA regulon
Original publications