Difference between revisions of "Obg"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
* '''Locus tag:''' BSU27920 | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU27920 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=obg_2852661_2853947_-1 Expression] | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 08:33, 26 January 2012
- Description: GTP-binding protein involved in initiation of sporulation and assembly of the 50S ribosome subunit
| Gene name | obg |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | Yes |
| Product | GTP-binding protein |
| Function | ribosome assembly, may be required to stimulate activity of the phosphorelay that activates Spo0A |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Obg | |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 4.859 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1284 bp, 428 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pheB, spo0B |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 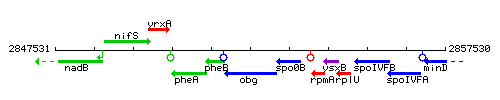
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
translation, phosphorelay, essential genes, GTP-binding proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27920
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Binds and hydrolyzes GTP and readily exchanges GDP for GTP
- Protein family: GTP1/OBG family (according to Swiss-Prot) Era/Obg family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
Obg possesses 3 domains: A N-terminal glycine-rich domain (1–158), a GTP binding domain (159–342) and a C-terminal TGS domain (343–428). The TGS domain has no known function, but it is named for three protein families in which it is found, ThrRS, GTPase, and SpoT.
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
GDP, GTP and probably ppGpp
- Effectors of protein activity:
Interaction with Rsb proteins.
Database entries
- UniProt: P20964
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
The biochemical analysis of bacterial and human Obg proteins combined with the structural observation of the ppGpp nucleotide within the Obg active site suggest a potential role for ppGpp modulation of Obg function in B. subtilis.
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Bill Haldenwang, San Antonio, USA
- Naotake Ogasawara, Nara, Japan
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications