Difference between revisions of "MurB"
(→Categories containing this gene/protein) |
(→Extended information on the protein) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' |
| − | * '''Localization:''' cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot) | + | * '''[[Localization]]:''' cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot) |
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
Revision as of 10:28, 2 November 2011
- Description: UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase
| Gene name | murB |
| Synonyms | ylxC |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase |
| Function | peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Cell wall | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 6.087 |
| Gene length, protein length | 909 bp, 303 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | murG, divIB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 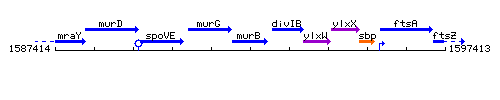
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, sporulation proteins, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigE regulon, SigM regulon, SpoIIID regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15230
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: UDP-N-acetylmuramate + NADP+ = UDP-N-acetyl-3-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-D-glucosamine + NADPH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FAD-binding PCMH-type domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P18579
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.158
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Adriano Henriques, Lisbon, Portugal homepage
Your additional remarks
References