Difference between revisions of "RocG"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[utilization of amino acids]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[trigger enzyme]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[AhrC regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[CcpA regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[RocR regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigL regulon]]}} | ||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
| Line 53: | Line 63: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 9 December 2010
- Description: trigger enzyme: catabolic glutamate dehydrogenase induced by arginine, ornithine or proline, subject to carbon catabolite repression
| Gene name | rocG |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: glutamate dehydrogenase (major) |
| Function | arginine utilization, controls the activity of GltC |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ammonium/ glutamate | |
| MW, pI | 46.2 kDa, 6.28 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1272 bp, 424 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | rocA, yweA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 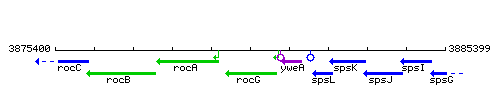
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of amino acids, trigger enzyme
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AhrC regulon, CcpA regulon, RocR regulon, SigL regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37790
Phenotypes of a mutant
Poor growth on complex media such as SP (sporulation medium). No growth in minimal media with arginine as the only carbon source. Rapid accumulation of suppressor mutants (gudB1)
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamate + H2O + NAD+ = 2-oxoglutarate + NH3 + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot) L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH, controls the activity of the GltC transcription activator PubMed
- Protein family: Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenases family (according to Swiss-Prot) Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenases family
- Paralogous protein(s): GudB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions: RocG-GltC, this interaction prevents transcription activation of the gltA-gltB operon by GltC PubMed
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 3K92 (super-repressor mutant that is capable of constitutive inactivation of GltC, E93K mutation) PubMed
- UniProt: P39633
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.2
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rocG PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Activation by RocR requires binding of RocR to a downstream element PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP747 (spc), GP726 (aphA3), GP810 (tet) available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody: available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Enzymatic activity of RocG
Katrin Gunka, Joseph A Newman, Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Cecilia Rodrigues, Lorraine Hewitt, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
Functional dissection of a trigger enzyme: mutations of the bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase RocG that affect differentially its catalytic activity and regulatory properties.
J Mol Biol: 2010, 400(4);815-27
[PubMed:20630473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeki Kada, Masahiro Yabusaki, Takayuki Kaga, Hitoshi Ashida, Ken-ichi Yoshida
Identification of two major ammonia-releasing reactions involved in secondary natto fermentation.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2008, 72(7);1869-76
[PubMed:18603778]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Katrin Gunka, Jens J Landmann, Jörg Stülke
Glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: gene expression and enzyme activities evolved to avoid futile cycles and to allow rapid responses to perturbations of the system.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(10);3557-64
[PubMed:18326565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Md Iqbal Hassan Khan, Kousuke Ito, Hyeung Kim, Hiroyuki Ashida, Takahiro Ishikawa, Hitoshi Shibata, Yoshihiro Sawa
Molecular properties and enhancement of thermostability by random mutagenesis of glutamate dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2005, 69(10);1861-70
[PubMed:16244435]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Iqbal Hassan Khan, Hyeung Kim, Hiroyuki Ashida, Takahiro Ishikawa, Hitoshi Shibata, Yoshihiro Sawa
Altering the substrate specificity of glutamate dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis by site-directed mutagenesis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2005, 69(9);1802-5
[PubMed:16195607]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, A L Sonenshein
Role and regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(23);6298-305
[PubMed:9829940]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Function in the control of GltC activity
Katrin Gunka, Joseph A Newman, Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Cecilia Rodrigues, Lorraine Hewitt, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
Functional dissection of a trigger enzyme: mutations of the bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase RocG that affect differentially its catalytic activity and regulatory properties.
J Mol Biol: 2010, 400(4);815-27
[PubMed:20630473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christina Herzberg, Lope Andrés Flórez Weidinger, Bastian Dörrbecker, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke, Fabian M Commichau
SPINE: a method for the rapid detection and analysis of protein-protein interactions in vivo.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(22);4032-5
[PubMed:17994626]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Philipp Tripal, Oliver Valerius, Jörg Stülke
A regulatory protein-protein interaction governs glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis: the glutamate dehydrogenase RocG moonlights in controlling the transcription factor GltC.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 65(3);642-54
[PubMed:17608797]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fabian M Commichau, Ingrid Wacker, Jan Schleider, Hans-Matti Blencke, Irene Reif, Philipp Tripal, Jörg Stülke
Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with carbon source-independent glutamate biosynthesis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2007, 12(1-2);106-13
[PubMed:17183217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Modulation of activity of Bacillus subtilis regulatory proteins GltC and TnrA by glutamate dehydrogenase.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(11);3399-407
[PubMed:15150225]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Expression of rocG
Structural analysis of glutamate dehydrogenase
Katrin Gunka, Joseph A Newman, Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Cecilia Rodrigues, Lorraine Hewitt, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
Functional dissection of a trigger enzyme: mutations of the bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase RocG that affect differentially its catalytic activity and regulatory properties.
J Mol Biol: 2010, 400(4);815-27
[PubMed:20630473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
T J Stillman, P J Baker, K L Britton, D W Rice
Conformational flexibility in glutamate dehydrogenase. Role of water in substrate recognition and catalysis.
J Mol Biol: 1993, 234(4);1131-9
[PubMed:8263917]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)