Difference between revisions of "RpmA"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 282 bp, 94 aa | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 282 bp, 94 aa | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[spo0B]]'', ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[spo0B]]'', ''[[prp]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU27940 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU27940 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU27940 DNA_with_flanks] | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU27940 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU27940 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU27940 DNA_with_flanks] | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 10 December 2014
- Description: ribosomal protein
| Gene name | rpmA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | ribosomal protein L27 (BL24) |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rpmA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RpmA | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 10.764 |
| Gene length, protein length | 282 bp, 94 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spo0B, prp |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 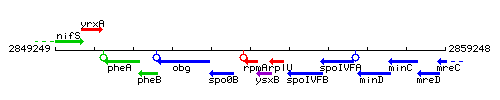
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed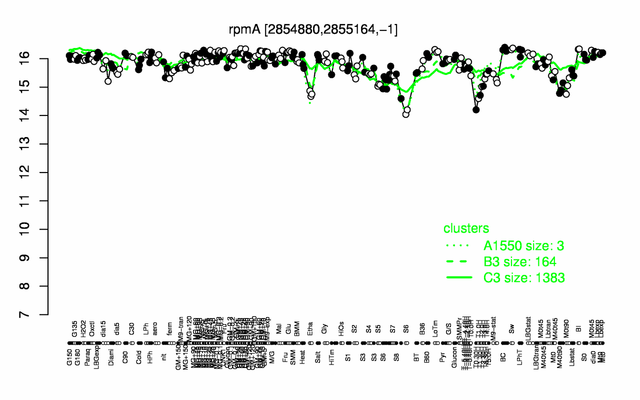
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27940
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU27940
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ribosomal protein L27P family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU27940
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05657
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- the protein is significantly underrepresented in 45S assembly intermediates that accumulate upon depletion of RbgA PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rpmA PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Erin A Wall, J Harry Caufield, Charles E Lyons, Keith A Manning, Terje Dokland, Gail E Christie
Specific N-terminal cleavage of ribosomal protein L27 in Staphylococcus aureus and related bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 2015, 95(2);258-69
[PubMed:25388641]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ahmad Jomaa, Nikhil Jain, Joseph H Davis, James R Williamson, Robert A Britton, Joaquin Ortega
Functional domains of the 50S subunit mature late in the assembly process.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2014, 42(5);3419-35
[PubMed:24335279]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Genki Akanuma, Hideaki Nanamiya, Yousuke Natori, Koichi Yano, Shota Suzuki, Shuya Omata, Morio Ishizuka, Yasuhiko Sekine, Fujio Kawamura
Inactivation of ribosomal protein genes in Bacillus subtilis reveals importance of each ribosomal protein for cell proliferation and cell differentiation.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(22);6282-91
[PubMed:23002217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew A Lauber, William E Running, James P Reilly
B. subtilis ribosomal proteins: structural homology and post-translational modifications.
J Proteome Res: 2009, 8(9);4193-206
[PubMed:19653700]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Wipat, N Carter, S C Brignell, B J Guy, K Piper, J Sanders, P T Emmerson, C R Harwood
The dnaB-pheA (256 degrees-240 degrees) region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome containing genes responsible for stress responses, the utilization of plant cell walls and primary metabolism.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 11);3067-78
[PubMed:8969504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)