Difference between revisions of "GlmS"
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
** subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | ** subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | ||
** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[glmM]]'' and ''[[glmS]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[glmM]]'' and ''[[glmS]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 340 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2741 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 09:55, 17 April 2014
- Description: glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase
| Gene name | glmS |
| Synonyms | gcaA, ybxD |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase |
| Function | cell wall synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: glmS | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: glmS | |
| MW, pI | 65 kDa, 4.796 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1800 bp, 600 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glmM, alkA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed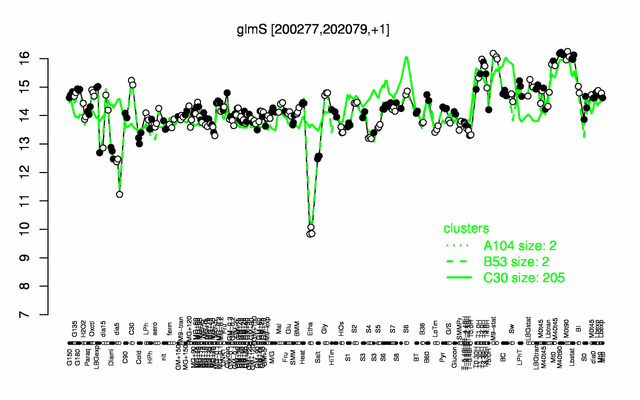
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01780
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01780
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamine + D-fructose 6-phosphate = L-glutamate + D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01780
- UniProt: P39754
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.6.1.16
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism: glmS ribozyme: glucosamine 6-phosphate binds the leader mRNA, and a riboswitch with ribozyme activity cleaves off the glmS section from the mRNA, resulting in stopp of transcript elongation
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- A ncRNA is predicted between glmM and glmS PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 340 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2741 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Wade Winkler, University of Texas, USA, Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Philippe Durand, Béatrice Golinelli-Pimpaneau, Stéphane Mouilleron, Bernard Badet, Marie-Ange Badet-Denisot
Highlights of glucosamine-6P synthase catalysis.
Arch Biochem Biophys: 2008, 474(2);302-17
[PubMed:18279655]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
The glmS Ribozyme
Christina E Lünse, Günter Mayer
Screening assays to identify artificial glmS ribozyme activators.
Methods Mol Biol: 2014, 1103;199-209
[PubMed:24318896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Krista M Brooks, Ken J Hampel
Rapid steps in the glmS ribozyme catalytic pathway: cation and ligand requirements.
Biochemistry: 2011, 50(13);2424-33
[PubMed:21395279]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Y Watson, Martha J Fedor
The glmS riboswitch integrates signals from activating and inhibitory metabolites in vivo.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2011, 18(3);359-63
[PubMed:21317896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jesse C Cochrane, Sarah V Lipchock, Kathryn D Smith, Scott A Strobel
Structural and chemical basis for glucosamine 6-phosphate binding and activation of the glmS ribozyme.
Biochemistry: 2009, 48(15);3239-46
[PubMed:19228039]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jennifer A Collins, Irnov Irnov, Stephanie Baker, Wade C Winkler
Mechanism of mRNA destabilization by the glmS ribozyme.
Genes Dev: 2007, 21(24);3356-68
[PubMed:18079181]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rebecca A Tinsley, Jennifer R W Furchak, Nils G Walter
Trans-acting glmS catalytic riboswitch: locked and loaded.
RNA: 2007, 13(4);468-77
[PubMed:17283212]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Kenneth Blount, Izabela Puskarz, Robert Penchovsky, Ronald Breaker
Development and application of a high-throughput assay for glmS riboswitch activators.
RNA Biol: 2006, 3(2);77-81
[PubMed:17114942]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniel J Klein, Adrian R Ferré-D'Amaré
Structural basis of glmS ribozyme activation by glucosamine-6-phosphate.
Science: 2006, 313(5794);1752-6
[PubMed:16990543]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ken J Hampel, Melissa M Tinsley
Evidence for preorganization of the glmS ribozyme ligand binding pocket.
Biochemistry: 2006, 45(25);7861-71
[PubMed:16784238]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Adam Roth, Ali Nahvi, Mark Lee, Inbal Jona, Ronald R Breaker
Characteristics of the glmS ribozyme suggest only structural roles for divalent metal ions.
RNA: 2006, 12(4);607-19
[PubMed:16484375]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tom J McCarthy, Melissa A Plog, Shennen A Floy, Joshua A Jansen, Juliane K Soukup, Garrett A Soukup
Ligand requirements for glmS ribozyme self-cleavage.
Chem Biol: 2005, 12(11);1221-6
[PubMed:16298301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jeffrey E Barrick, Keith A Corbino, Wade C Winkler, Ali Nahvi, Maumita Mandal, Jennifer Collins, Mark Lee, Adam Roth, Narasimhan Sudarsan, Inbal Jona, J Kenneth Wickiser, Ronald R Breaker
New RNA motifs suggest an expanded scope for riboswitches in bacterial genetic control.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2004, 101(17);6421-6
[PubMed:15096624]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Wade C Winkler, Ali Nahvi, Adam Roth, Jennifer A Collins, Ronald R Breaker
Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme.
Nature: 2004, 428(6980);281-6
[PubMed:15029187]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Other Original Publications