Difference between revisions of "SinR"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| Line 128: | Line 127: | ||
* '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=sinR_2552653_2552988_1 sinR] {{PubMed|22383849}} | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=sinR_2552653_2552988_1 sinR] {{PubMed|22383849}} | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
** ''[[sinI]]'': [[SigA]] {{PubMed|3125149}} | ** ''[[sinI]]'': [[SigA]] {{PubMed|3125149}} | ||
** ''[[sinR]]'': [[SigA]] {{PubMed|3125149}} | ** ''[[sinR]]'': [[SigA]] {{PubMed|3125149}} | ||
| Line 171: | Line 170: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed>20395361 20541494 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>20395361 20541494 23353768 </pubmed> |
==Modelling of the [[SinI]]/[[SinR]] switch== | ==Modelling of the [[SinI]]/[[SinR]] switch== | ||
<pubmed> 21095906 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 21095906 </pubmed> | ||
Revision as of 10:02, 1 February 2013
- Description: transcriptional regulator of post-exponential-phase responses genes
| Gene name | sinR |
| Synonyms | sin, flaD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator of post-exponential-phase responses genes |
| Function | control of biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sinR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SinR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm, Central C-metabolism, Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 12 kDa, 7.177 |
| Gene length, protein length | 333 bp, 111 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sinI, tasA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 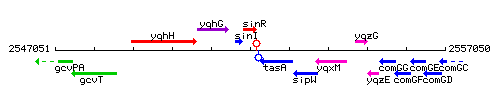
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, transition state regulators, biofilm formation
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, ScoC regulon, Spo0A regulon
The SinR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcription repressor of biofilm genes, acts as co-repressor for SlrR PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): SlrR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P06533
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: TMB079 sinR::spec, GP736 (tetR), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Hera Vlamakis, Yunrong Chai, Pascale Beauregard, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2013, 11(3);157-68
[PubMed:23353768]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patrick Piggot
Epigenetic switching: bacteria hedge bets about staying or moving.
Curr Biol: 2010, 20(11);R480-2
[PubMed:20541494]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David Dubnau
Swim or chill: lifestyles of a bacillus.
Genes Dev: 2010, 24(8);735-7
[PubMed:20395361]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Modelling of the SinI/SinR switch
Jennifer S Hallinan, Goksel Misirli, Anil Wipat
Evolutionary computation for the design of a stochastic switch for synthetic genetic circuits.
Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc: 2010, 2010;768-74
[PubMed:21095906]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Additonal publications: PubMed
Diethmaier C, Pietack N, Gunka K, Wrede C, Lehnik-Habrink M, Herzberg C, Hübner S, Stülke J A Novel Factor Controlling Bistability in Bacillus subtilis: The YmdB Protein Affects Flagellin Expression and Biofilm Formation. J Bacteriol.: 2011, 193(21):5997-6007. PubMed:21856853
Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol Microbiol. 2011 81(6): 1459-1473. PubMed:21815947