Difference between revisions of "GuaB"
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| + | ** inhibition of enzymatic activity by (p)ppGpp during the ´stringent response´{{PubMed|6111556}} | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
| Line 118: | Line 119: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
** activated during growth in the presence of branched chain amino acids ([[CodY]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ** activated during growth in the presence of branched chain amino acids ([[CodY]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ||
| − | |||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
** [[CodY]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ** [[CodY]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Additional information:''' the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12884008 PubMed] | + | * '''Additional information:''' |
| + | ** the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12884008 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** inhibition of enzymatic activity by (p)ppGpp during the ´stringent response´{{PubMed|6111556}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 146: | Line 148: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>17611193,12884008,1722815,,12618455,17726680 17726680 | + | <pubmed>17611193,12884008,1722815,,12618455,17726680 17726680 6111556 </pubmed> |
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/PMID PubMed] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/PMID PubMed] | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:38, 25 July 2012
- Description: IMP dehydrogenase
| Gene name | guaB |
| Synonyms | guaA |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | IMP dehydrogenase |
| Function | biosynthesis of GMP |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Purine synthesis, Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 52 kDa, 6.168 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1464 bp, 488 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yaaC, dacA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 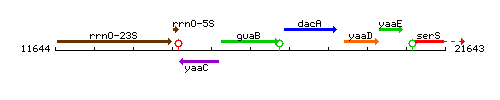
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of nucleotides, essential genes, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00090
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD+ + H2O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: IMPDH/GMPR family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- inhibition of enzymatic activity by (p)ppGpp during the ´stringent response´PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 1VRD (from Thermotoga maritima msb8, 60% identity, 80% similarity)
- UniProt: P21879
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.205
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: guaB PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References