Difference between revisions of "VmlR"
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
| Line 106: | Line 103: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| + | ** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[vmlR]]'' and ''[[ydgF]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 127: | Line 125: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>10092453,16109936 , </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>10092453,16109936 , 20525796</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:30, 4 May 2011
- Description: ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein), efflux of antibiotics (virginiamycin M, lincomycin)
| Gene name | vmlR |
| Synonyms | expZ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | antibiotic efflux ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein) |
| Function | efflux of antibiotics (virginiamycin M, lincomycin) |
| MW, pI | 62 kDa, 6.727 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1641 bp, 547 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ydgE, ydgF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 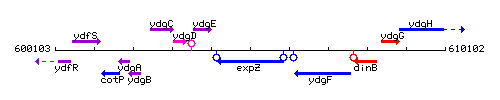
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, resistance against toxins/ antibiotics
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU05610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ABC transporter family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39115
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: vmlR PubMed
- Regulation: induced by virginiamycin M or lincomycin PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: transcriptional antitermination, details are unknown PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Reiko Ohki, Kozue Tateno, Teruaki Takizawa, Toshiko Aiso, Makiko Murata
Transcriptional termination control of a novel ABC transporter gene involved in antibiotic resistance in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(17);5946-54
[PubMed:16109936]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)