Difference between revisions of "MurE"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/bsu/BSU15180 murE] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/lys_threo.html Lys, Thr], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/cellwall.html Cell wall]''' | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/lys_threo.html Lys, Thr], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/cellwall.html Cell wall]''' | ||
Revision as of 09:22, 7 August 2012
- Description: UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diaminopimelate synthetase
| Gene name | murE |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl- meso-2,6-diaminopimelate synthetase |
| Function | peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: murE | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Lys, Thr, Cell wall | |
| MW, pI | 54 kDa, 5.558 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1482 bp, 494 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spoVD, mraY |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed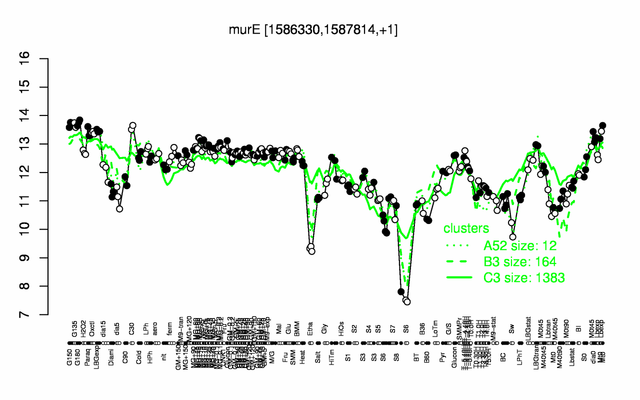
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15180
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate + meso-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-gamma-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diamino-heptanedioate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: MurE subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: Q03523
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.3.2.13
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Jean van Heijenoort
Lipid intermediates in the biosynthesis of bacterial peptidoglycan.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2007, 71(4);620-35
[PubMed:18063720]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R A Daniel, J Errington
DNA sequence of the murE-murD region of Bacillus subtilis 168.
J Gen Microbiol: 1993, 139(2);361-70
[PubMed:8436954]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A O Henriques, H de Lencastre, P J Piggot
A Bacillus subtilis morphogene cluster that includes spoVE is homologous to the mra region of Escherichia coli.
Biochimie: 1992, 74(7-8);735-48
[PubMed:1391053]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)