PgpH
- Description: c-di-AMP specific phosphodiesterase
| Gene name | pgpH |
| Synonyms | yqfF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | c-di-AMP specific phosphodiesterase |
| Function | control of c-di-AMP homeostasis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pgpH | |
| MW, pI | 78 kDa, 7.697 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2133 bp, 711 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqfG, phoH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 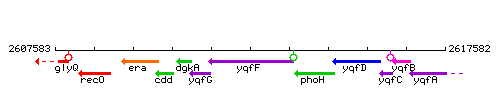
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed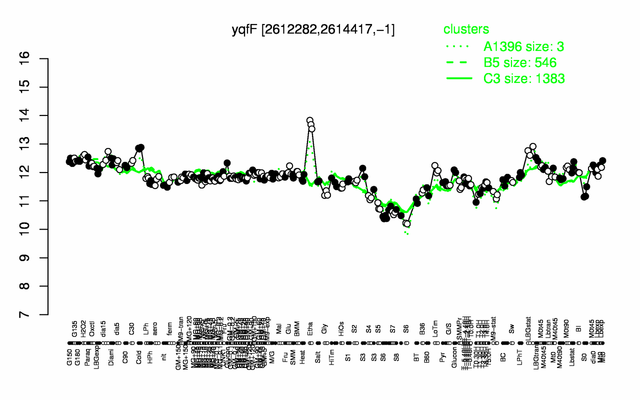
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
metabolism of signalling nucleotides, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU25330
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25330
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- hydrolysis of c-di-AMP to 5'-pApA PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Cofactors: Mn(2+) PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- ppGpp acts as allosteric inhibitor of phosphodiesterase activity (in Listeria monocytogenes) PubMed
- Interactions:
- PgpH is a member of a suspected group of hubs proteins that were suggested to be involved in a large number of interactions PubMed
- Localization:
- cell membrane PubMed (according to UniProt)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25330
- Structure:
- UniProt: P46344
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- SM-GN1 (yqfF-spc), available in Anne Galinier's and Boris Görke's labs
- BKE25330 (yqfF::erm without terminator, available in the BGSC and in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- GP2033 (yqfF::tet, available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- GP2034 (yqfF::erm without terminator, available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- GP2049 (yqfF::cat without terminator, available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications