OpuBA
- Description: choline ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein)
| Gene name | opuBA |
| Synonyms | proV |
| Essential | no |
| Product | choline ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein) |
| Function | compatible solute transport |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: opuBA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: OpuBA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: opuBA | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 5.654 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1143 bp, 381 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | opuBB, yvaV |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 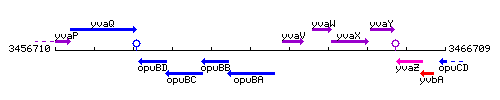
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed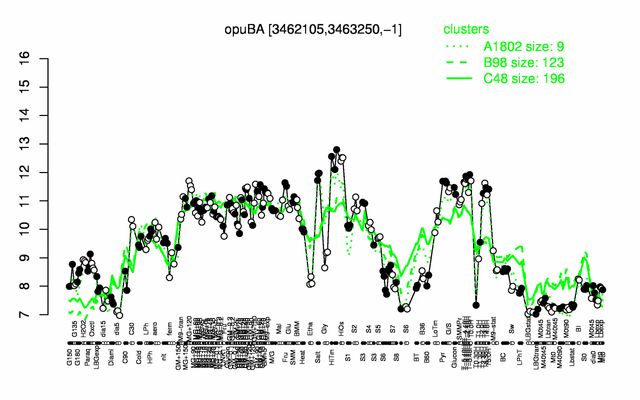
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, coping with hyper-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
GbsR regulon, OpcR regulon, RemA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33730
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU33730
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ABC transporter family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): OpuCA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: associated to the membrane (via OpuBB-OpuBD) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU33730
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q45460
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 42 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 109 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 215 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 271 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 161 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Chun-Hao Lee, Tien-Yu Wu, Gwo-Chyuan Shaw
Involvement of OpcR, a GbsR-type transcriptional regulator, in negative regulation of two evolutionarily closely related choline uptake genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2013, 159(Pt 10);2087-2096
[PubMed:23960087]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jared T Winkelman, Anna C Bree, Ashley R Bate, Patrick Eichenberger, Richard L Gourse, Daniel B Kearns
RemA is a DNA-binding protein that activates biofilm matrix gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(5);984-97
[PubMed:23646920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gabriele Nau-Wagner, Daniela Opper, Anne Rolbetzki, Jens Boch, Bettina Kempf, Tamara Hoffmann, Erhard Bremer
Genetic control of osmoadaptive glycine betaine synthesis in Bacillus subtilis through the choline-sensing and glycine betaine-responsive GbsR repressor.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(10);2703-14
[PubMed:22408163]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tamara Hoffmann, Erhard Bremer
Protection of Bacillus subtilis against cold stress via compatible-solute acquisition.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(7);1552-62
[PubMed:21296969]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
R M Kappes, B Kempf, S Kneip, J Boch, J Gade, J Meier-Wagner, E Bremer
Two evolutionarily closely related ABC transporters mediate the uptake of choline for synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 32(1);203-16
[PubMed:10216873]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Nau-Wagner, J Boch, Le Good JA, E Bremer
High-affinity transport of choline-O-sulfate and its use as a compatible solute in Bacillus subtilis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 1999, 65(2);560-8
[PubMed:9925583]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)