Pta
- Description: phosphotransacetylase
| Gene name | pta |
| Synonyms | ipa-88d, ywfJ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | phosphotransacetylase |
| Function | overflow metabolism |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pta | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: pta | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 4.649 |
| Gene length, protein length | 969 bp, 323 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cysL, ywfI |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 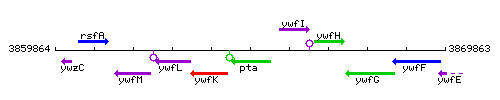
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed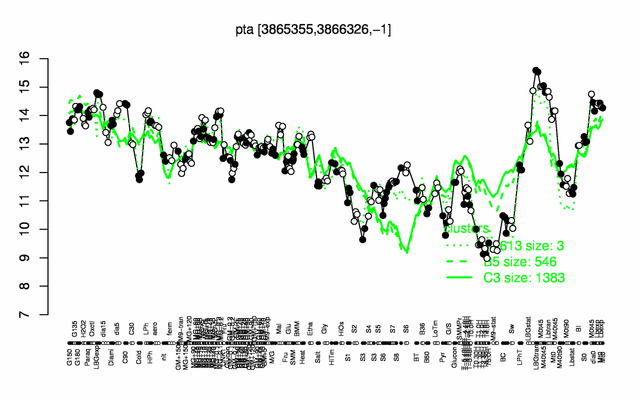
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37660
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37660
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + phosphate = CoA + acetyl phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: phosphate acetyltransferase and butyryltransferase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on (Ser-123 OR Thr-128 OR Ser-129) PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37660
- UniProt: P39646
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.1.8
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: pta PubMed
- Regulation:
- expression activated by glucose (2.6 fold) (CcpA) PubMed
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2825 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 7432 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 2878 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1417 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1754 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP668 (aphA3), available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
V K Morya, Varun Dewaker, Eun-Ki Kim
In silico study and validation of phosphotransacetylase (PTA) as a putative drug target for Staphylococcus aureus by homology-based modelling and virtual screening.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol: 2012, 168(7);1792-805
[PubMed:23054816]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Qian Steven Xu, Jarmila Jancarik, Yun Lou, Kate Kuznetsova, Alexander F Yakunin, Hisao Yokota, Paul Adams, Rosalind Kim, Sung-Hou Kim
Crystal structures of a phosphotransacetylase from Bacillus subtilis and its complex with acetyl phosphate.
J Struct Funct Genomics: 2005, 6(4);269-79
[PubMed:16283428]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Presecan-Siedel, A Galinier, R Longin, J Deutscher, A Danchin, P Glaser, I Martin-Verstraete
Catabolite regulation of the pta gene as part of carbon flow pathways in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(22);6889-97
[PubMed:10559153]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B S Shin, S K Choi, S H Park
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis phosphotransacetylase gene.
J Biochem: 1999, 126(2);333-9
[PubMed:10423526]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)