FtsZ
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation)
| Gene name | ftsZ |
| Synonyms | ts-1 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division initiation protein (septum formation) |
| Function | formation of Z-ring |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ftsZ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FtsZ | |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 4.814 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1146 bp, 382 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsA, bpr |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed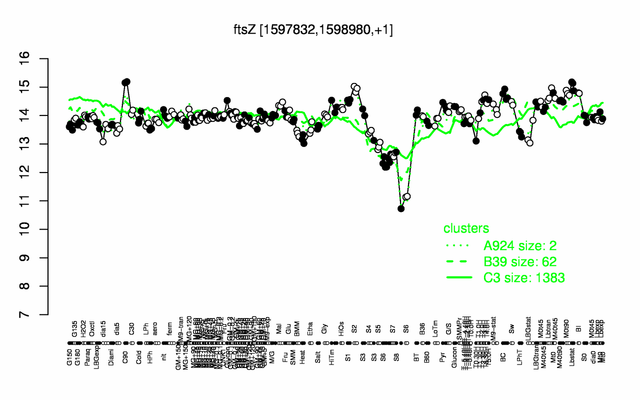
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15290
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU15290
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsZ family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Z ring formation is inhibited upon binding of MciZ to FtsZ
- bundling of FtsZ protofilaments into strikingly long and regular tubular structures reminiscent of eukaryotic microtubules requires the prior formation of large ring polymers of SepF PubMed
- interaction with UgtP inhibits FtsZ filament formation PubMed
- FtsZ polymerization is inhibited by interaction with MinC PubMed
- Localization:
- septal at the cell membrane PubMed
- septal localization partially depends on the proton motive force PubMed
- Noc and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring Z ring placement PubMed
- FtsZ is anchored to the cell membrane by either FtsA or SepF PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU15290
- UniProt: P17865
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- strains:
- GP1372 (Pxyl ftsZ aphA3) disA::tet cdaS::ermC for xylose inducible expression of ftsZ, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Imrich Barak, Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia homepage
- Leendert Hamoen, CBCB, Newcastle University, UK
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
FtsZ as antibacterial drug target
Filipa Marcelo, Sonia Huecas, Laura B Ruiz-Ávila, F Javier Cañada, Almudena Perona, Ana Poveda, Sonsoles Martín-Santamaría, Antonio Morreale, Jesús Jiménez-Barbero, José M Andreu
Interactions of bacterial cell division protein FtsZ with C8-substituted guanine nucleotide inhibitors. A combined NMR, biochemical and molecular modeling perspective.
J Am Chem Soc: 2013, 135(44);16418-28
[PubMed:24079270]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Laura B Ruiz-Avila, Sonia Huecas, Marta Artola, Albert Vergoñós, Erney Ramírez-Aportela, Emilia Cercenado, Isabel Barasoain, Henar Vázquez-Villa, Mar Martín-Fontecha, Pablo Chacón, María L López-Rodríguez, José M Andreu
Synthetic inhibitors of bacterial cell division targeting the GTP-binding site of FtsZ.
ACS Chem Biol: 2013, 8(9);2072-83
[PubMed:23855511]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Anusri Bhattacharya, Bhavya Jindal, Parminder Singh, Anindya Datta, Dulal Panda
Plumbagin inhibits cytokinesis in Bacillus subtilis by inhibiting FtsZ assembly--a mechanistic study of its antibacterial activity.
FEBS J: 2013, 280(18);4585-99
[PubMed:23841620]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David W Adams, Ling Juan Wu, Lloyd G Czaplewski, Jeff Errington
Multiple effects of benzamide antibiotics on FtsZ function.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(1);68-84
[PubMed:21276094]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Simranjeet Kaur, Niraj H Modi, Dulal Panda, Nilanjan Roy
Probing the binding site of curcumin in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis FtsZ--a structural insight to unveil antibacterial activity of curcumin.
Eur J Med Chem: 2010, 45(9);4209-14
[PubMed:20615583]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumiko W Shimotohno, Fujio Kawamura, Yousuke Natori, Hideaki Nanamiya, Junji Magae, Hiromitsu Ogata, Toyoshige Endo, Takeshi Suzuki, Hiroshi Yamaki
Inhibition of septation in Bacillus subtilis by a peptide antibiotic, edeine B(1).
Biol Pharm Bull: 2010, 33(4);568-71
[PubMed:20410587]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
José M Andreu, Claudia Schaffner-Barbero, Sonia Huecas, Dulce Alonso, María L Lopez-Rodriguez, Laura B Ruiz-Avila, Rafael Núñez-Ramírez, Oscar Llorca, Antonio J Martín-Galiano
The antibacterial cell division inhibitor PC190723 is an FtsZ polymer-stabilizing agent that induces filament assembly and condensation.
J Biol Chem: 2010, 285(19);14239-46
[PubMed:20212044]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tushar K Beuria, Parminder Singh, Avadhesha Surolia, Dulal Panda
Promoting assembly and bundling of FtsZ as a strategy to inhibit bacterial cell division: a new approach for developing novel antibacterial drugs.
Biochem J: 2009, 423(1);61-9
[PubMed:19583568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Neil R Stokes, Jörg Sievers, Stephanie Barker, James M Bennett, David R Brown, Ian Collins, Veronica M Errington, David Foulger, Michelle Hall, Rowena Halsey, Hazel Johnson, Valerie Rose, Helena B Thomaides, David J Haydon, Lloyd G Czaplewski, Jeff Errington
Novel inhibitors of bacterial cytokinesis identified by a cell-based antibiotic screening assay.
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(48);39709-15
[PubMed:16174771]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Other original Publications