MtnK
- Description: 5-methylthioribose kinase
| Gene name | mtnK |
| Synonyms | ykrT |
| Essential | no |
| Product | 5-methylthioribose kinase |
| Function | methionine salvage |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mtnK | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: mtnK | |
| MW, pI | 45 kDa, 4.856 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1197 bp, 399 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mtnA, mtnU |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 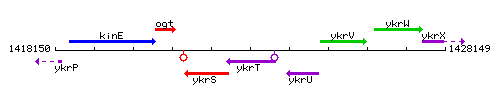
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed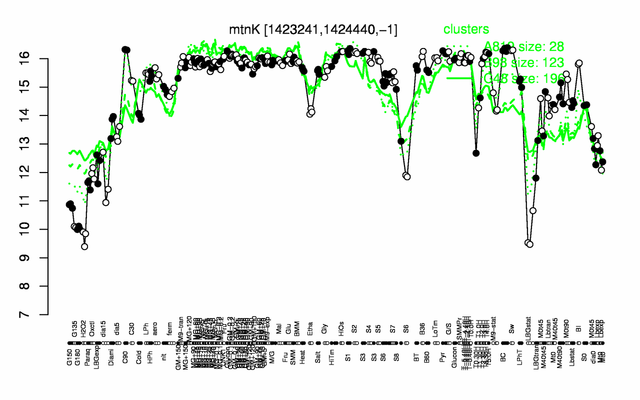
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13560
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + S-methyl-5-thio-D-ribose = ADP + S-methyl-5-thio-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: methylthioribose kinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-80 OR Arg-82 and Arg-365 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane associated PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 2PUP
- UniProt: O31663
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.100
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism: S-box: transcription termination/ antitermination, the S-box riboswitch binds S-adenosylmethionine resulting in termination PubMed
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Toshihiro Nakano, Yohtaro Saito, Akiho Yokota, Hiroki Ashida
Plausible novel ribose metabolism catalyzed by enzymes of the methionine salvage pathway in Bacillus subtilis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2013, 77(5);1104-7
[PubMed:23649237]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jerneja Tomsic, Brooke A McDaniel, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin
Natural variability in S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent riboswitches: S-box elements in bacillus subtilis exhibit differential sensitivity to SAM In vivo and in vitro.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(3);823-33
[PubMed:18039762]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Agnieszka Sekowska, Valérie Dénervaud, Hiroki Ashida, Karine Michoud, Dieter Haas, Akiho Yokota, Antoine Danchin
Bacterial variations on the methionine salvage pathway.
BMC Microbiol: 2004, 4;9
[PubMed:15102328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Maumita Mandal, Benjamin Boese, Jeffrey E Barrick, Wade C Winkler, Ronald R Breaker
Riboswitches control fundamental biochemical pathways in Bacillus subtilis and other bacteria.
Cell: 2003, 113(5);577-86
[PubMed:12787499]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Agnieszka Sekowska, Antoine Danchin
The methionine salvage pathway in Bacillus subtilis.
BMC Microbiol: 2002, 2;8
[PubMed:12022921]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Brooke A Murphy, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin
Prediction of gene function in methylthioadenosine recycling from regulatory signals.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(8);2314-8
[PubMed:11914366]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Sekowska, L Mulard, S Krogh, J K Tse, A Danchin
MtnK, methylthioribose kinase, is a starvation-induced protein in Bacillus subtilis.
BMC Microbiol: 2001, 1;15
[PubMed:11545674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
The S box regulon: a new global transcription termination control system for methionine and cysteine biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 30(4);737-49
[PubMed:10094622]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)