SpoIIIJ
- Description: Sec-independent membrane protein translocase, essential for SigG activity at stage III
| Gene name | spoIIIJ |
| Synonyms | spo0J87 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | membrane protein translocase |
| Function | membrane insertion of proteins and protein secretion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIIJ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIIIJ | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 9.992 |
| Gene length, protein length | 783 bp, 261 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | jag, rnpA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 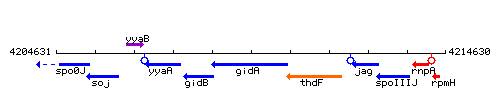
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, sporulation/ other, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU41040
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: membrane protein translocase, facilitates insertion of SpoIIIAE into the membrane PubMed
- Protein family: Type 2 subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q01625
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard University, Cambridge, USA homepage
Adriano Henriques, Lisbon, Portugal homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Ross E Dalbey, Peng Wang, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Membrane proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(2);311-30
[PubMed:22688815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Markus Birkenmeier, Susanne Neumann, Thorsten Röder
Kinetic modeling of riboflavin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis under production conditions.
Biotechnol Lett: 2014, 36(5);919-28
[PubMed:24442413]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Chun-Kai Yang, Chung-Dar Lu, Phang C Tai
Differential expression of secretion machinery during bacterial growth: SecY and SecF decrease while SecA increases during transition from exponential phase to stationary phase.
Curr Microbiol: 2013, 67(6);682-7
[PubMed:23852076]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shinobu Chiba, Koreaki Ito
Multisite ribosomal stalling: a unique mode of regulatory nascent chain action revealed for MifM.
Mol Cell: 2012, 47(6);863-72
[PubMed:22864117]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shinobu Chiba, Anne Lamsa, Kit Pogliano
A ribosome-nascent chain sensor of membrane protein biogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 2009, 28(22);3461-75
[PubMed:19779460]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Manfred J Saller, Fabrizia Fusetti, Arnold J M Driessen
Bacillus subtilis SpoIIIJ and YqjG function in membrane protein biogenesis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(21);6749-57
[PubMed:19717609]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mónica Serrano, Filipe Vieira, Charles P Moran, Adriano O Henriques
Processing of a membrane protein required for cell-to-cell signaling during endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(23);7786-96
[PubMed:18820020]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Amy H Camp, Richard Losick
A novel pathway of intercellular signalling in Bacillus subtilis involves a protein with similarity to a component of type III secretion channels.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 69(2);402-17
[PubMed:18485064]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Helena B Thomaides, Ella J Davison, Lisa Burston, Hazel Johnson, David R Brown, Alison C Hunt, Jeffery Errington, Lloyd Czaplewski
Essential bacterial functions encoded by gene pairs.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(2);591-602
[PubMed:17114254]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Aileen Rubio, Xin Jiang, Kit Pogliano
Localization of translocation complex components in Bacillus subtilis: enrichment of the signal recognition particle receptor at early sporulation septa.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(14);5000-2
[PubMed:15995216]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mónica Serrano, Luísa Côrte, Jason Opdyke, Charles P Moran, Adriano O Henriques
Expression of spoIIIJ in the prespore is sufficient for activation of sigma G and for sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(13);3905-17
[PubMed:12813085]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Harold Tjalsma, Sierd Bron, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Complementary impact of paralogous Oxa1-like proteins of Bacillus subtilis on post-translocational stages in protein secretion.
J Biol Chem: 2003, 278(18);15622-32
[PubMed:12586834]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Takako Murakami, Koki Haga, Michio Takeuchi, Tsutomu Sato
Analysis of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIIJ gene and its Paralogue gene, yqjG.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(7);1998-2004
[PubMed:11889108]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Errington, L Appleby, R A Daniel, H Goodfellow, S R Partridge, M D Yudkin
Structure and function of the spoIIIJ gene of Bacillus subtilis: a vegetatively expressed gene that is essential for sigma G activity at an intermediate stage of sporulation.
J Gen Microbiol: 1992, 138(12);2609-18
[PubMed:1487728]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)