FtsZ
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation)
| Gene name | ftsZ |
| Synonyms | ts-1 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division initiation protein (septum formation) |
| Function | formation of Z-ring |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ftsZ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FtsZ | |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 4.814 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1146 bp, 382 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsA, bpr |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 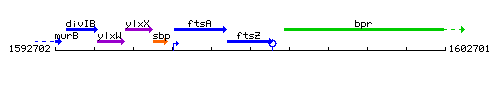
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed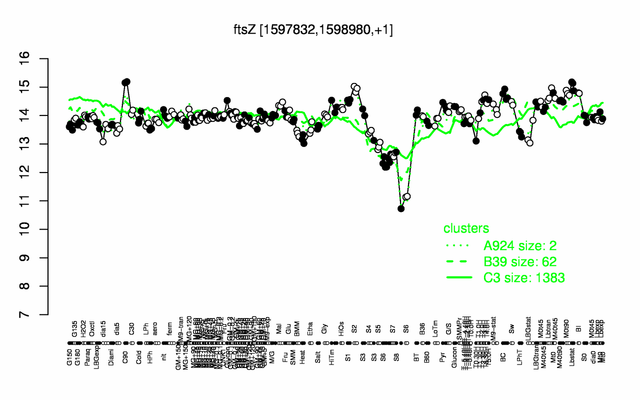
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15290
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsZ family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Z ring formation is inhibited upon binding of MciZ to FtsZ
- bundling of FtsZ protofilaments into strikingly long and regular tubular structures reminiscent of eukaryotic microtubules requires the prior formation of large ring polymers of SepF PubMed
- interaction with UgtP inhibits FtsZ filament formation PubMed
- FtsZ polymerization is inhibited by interaction with MinC PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P17865
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- strains:
- GP1372 (Pxyl ftsZ aphA3) disA::tet cdaS::ermC for xylose inducible expression of ftsZ, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Imrich Barak, Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia homepage
- Leendert Hamoen, CBCB, Newcastle University, UK
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
FtsZ as antibacterial drug target
Other original Publications