SrfAD
Revision as of 09:27, 14 May 2013 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: surfactin synthetase / competence
| Gene name | srfAD |
| Synonyms | comL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | surfactin synthetase / competence |
| Function | antibiotic synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: srfAD | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.22 |
| Gene length, protein length | 726 bp, 242 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | srfAC, ycxA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 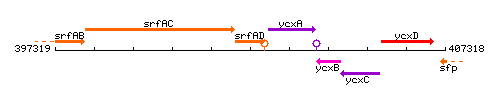
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
miscellaneous metabolic pathways, biosynthesis of antibacterial compounds
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Abh regulon, CodY regulon, ComA regulon, PerR regulon, Spx regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU03520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: thioesterase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: Q08788
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Massimiliano Marvasi, Pieter T Visscher, Lilliam Casillas Martinez
Exopolymeric substances (EPS) from Bacillus subtilis: polymers and genes encoding their synthesis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2010, 313(1);1-9
[PubMed:20735481]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed