SlrR
Revision as of 13:55, 13 May 2013 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: transcriptional activator of competence development and sporulation genes, represses SigD-dependent flagellar genes, antagonist of SlrA and SinR, has LexA-like autocleavage activity
| Gene name | slrR |
| Synonyms | yveJ, slr |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription regulator, SlrA antagonist |
| Function | regulation of initiation of biofilm formation and of autolysis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: slrR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SlrR | |
| Regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 9.63 |
| Gene length, protein length | 456 bp, 152 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | epsA, pnbA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 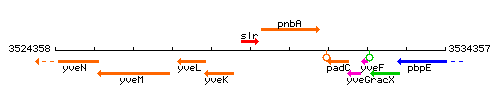
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed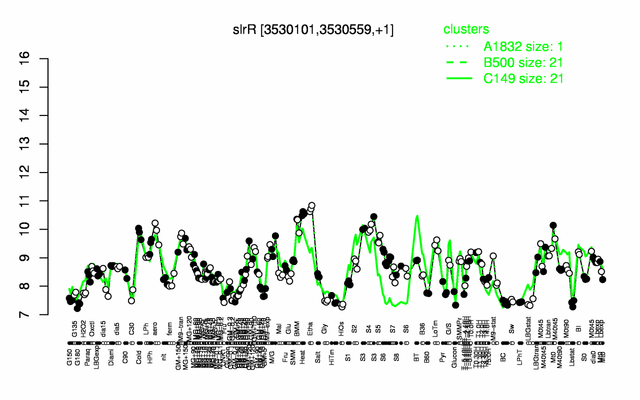
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, transition state regulators, biofilm formation
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Abh regulon, AbrB regulon, SinR regulon
The SlrR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34380
Phenotypes of a mutant
- smooth colonies on MsGG medium, no biofilm formation PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- SlrR binds to and inhibits the activity of SlrA, SlrA indirectly stimulates the synthesis of SlrR by interacting with SinR. SlrR can bind to SinR and SinR directly represses the transcription of SlrR. SlrR indirectly derepresses its own gene. The heterocomplex of SlrR-SinR is a repressor of autolysin and motility genes and inhibits the repressor function of SinR. PubMed
- repression of transcription of lytA-lytB-lytC and lytF PubMed
- autocleavage PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): SinR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: interaction with SinR triggers binding of SlrR to the promoters of lytA-lytB-lytC and lytF, resulting in their repression PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P71049
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP955 (slrR-pnbA::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications